What is TCP/IP Model?
Let us have a look at the topics covered in this article:
- What is TCP/IP Model?
- History of TCP/IP Model
- Why is TCP/IP Model important?
- TCP/IP Model Layers
- Advantages of TCP/IP Model
- Disadvantages of TCP/IP Model
- OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model
- Conclusion
Before going any further, look at this video in which our Cyber Security specialists explain the nitty-gritty of network security in detail:
What is TCP/IP Model?
The transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) model finds its origins in the ARPANET reference model. The architecture[1] [2] of TCP has evolved from studies in methods for connecting multiple packet-switched networks. The central aim of the TCP/IP model is to enable the sending of data packets to one application on a single computer. The TCP/IP model is an internet-capable set of protocols.
The TCP/IP model sets out how packets exchange information through the web. This set of communication protocols determines how data is to be broken, addressed, transferred, routed, and received for sharing. The server-client model is the communication model for this [3] [4] set.
The TCP/IP model describes how to construct communication lines for applications. It also manages to divide a message into packets before it is sent across and reassembled. IP outlines how packets are addressed and routed to make sure that the data reaches the right destination. The current internet architecture uses this network concept.
History of TCP/IP Model
At first, TCP was designed to meet the data communication needs of the US Department of Defense, also referred to as DoD. This finding began in the late 1960s when ARPA entered into a cooperation with US universities and industry research groups to design open standard protocols and establish multi-supplier networks. The initial host for most communication protocols created by ARPANET was Network Control Program (NCP.)
However, NCP has been unable to maintain the increasing traffic demand overtime. In 1974, ARPANET devised and built a new, more robust series of communication protocols based on TCP for communication in all areas. In the early version of this technology, there was only one core protocol called TCP.
In 1975, a two-network TCP/IP test was conducted between Stanford and University
College London. In 1982, the United States DoD declared TCP/IP as the standard for all military computer networking.
Why is TCP/IP Model important?
TCP/IP is unpatented and, as a result, is not controlled by any single company. The IP suite can thus be simply updated. It is interoperable with all operating systems and can interface with every other machine. The IP suite has complete computer hardware and internet compatibility.
TCP/IP is broadly accessible and enables the most efficient network path to be defined as a routable protocol.
Want to be a Certified Ethical Hacker. Join our Ethical Hacking Certification Course Today!
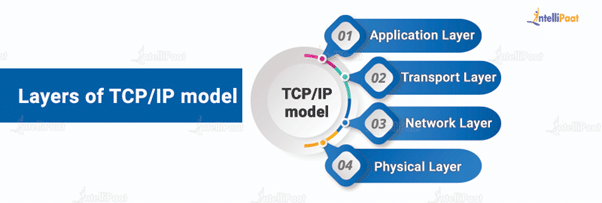
TCP/IP Model Layers

The TCP/IP model has four layers:
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Network Layer
- Physical Layer
Application Layer
The application layer is a combination of the application, presentation, and session layers. This layer is responsible for interaction between the user and the application. Here, data is formatted, converted, encrypted, decrypted, and set to the user.
Protocols used by the application layer are:
- HTTP: Hypertext transfer protocol allows the users to interact with the World Wide Web through browser applications.
- SMTP: Simple mail transfer protocol is used to send mails.
- FTP: File transfer protocol is used for transmitting files from one system to another.
- DNS: Domain name system is the phonebook of the internet.
- TELNET: Teletype network acts as a client-server protocol. It is used to provide bidirectional connection.

Transport Layer
The transport layer is responsible for end-to-end communication and provides error-free delivery of data. This layer can transport the data through a connection-oriented or connectionless layer.
The two protocols used in the transport layer are user datagram protocol (UDP) and TCP.
- UDP: This protocol provides connectionless service and end-to-end delivery of transmission. It is considered an unstable protocol because it discovers the errors but does not specify them.
- TCP: It provides all transport services to the application layer. TCP is a dependable protocol for error detection and retransmission. It assures that all segments must be received and recognized before completing the transmission and discarding the virtual circuit.
Network Layer
The network layer provides host addressing and chooses the best path to the destination network. This layer maintains the quality of service and offers connectionless end-to-end networking.
The protocols in the network layer are:
- IPV4: Internet protocol version 4 is employed for packetizing, forwarding, and delivery of packets. IP is an unreliable datagram protocol.
- ICMPV4: Interrupt control message protocol controls all errors. These mistakes are handled by ICMP protocol during the delivery of the message to target problems.
- IGMP: Internet group management protocol helps in multicasting.
Physical Layer
The physical layer interacts with the top level of the TCP/IP model application. This layer is the nearest end-user TCP/IP layer. It means that the consumers can connect with other software apps.
The physical layer interacts with software applications to develop media platforms. Data is constantly beyond the boundaries of the TCP/IP model to be interpreted in the application. An application such as a data transfer, mail, remote login, etc., is an example of this layer.
Career Transition
Preparing for an ethical hacking job interview? Have a look at our blog on Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and start preparing!
Advantages of TCP/IP Model
- It is an industry-standard model that can be effectively deployed in practical networking problems.
- It is interoperable, i.e., it allows cross-platform communications among heterogeneous networks.
- It is an open protocol suite and is not owned by any particular institute; so, it can be used by any individual or organization.
- It is a scalable, client-server architecture. It allows networks to be added without disturbing the current services.
- It assigns an IP address to each computer on the network, thus making each device to be identifiable over the network.
- It assigns each site a domain name; it provides name and address resolution services.
Disadvantages of TCP/IP Model
- It is not generic. So, it fails to represent any protocol stack other than the TCP/IP suite. For example, it cannot describe the Bluetooth connection.
- It does not separate the concepts of services, interfaces, and protocols. So, it is not suitable to describe new technologies in new networks.
- It does not distinguish between the data link and the physical layers, which have very different functionalities. The data link layer should concern with the transmission of frames. On the other hand, the physical layer should lay down the physical characteristics of the transmission. A proper model should segregate the two layers.
- It was originally designed and implemented for wide-area networks. It is not optimized and implemented for wide-area networks. It is not optimized for small networks such as local area network (LAN) and personal area network (PAN.)
- Among its suite of protocols, TCP and IP were carefully designed and well implemented. Some of the protocols were developed ad hoc and proved to be unsuitable in the long run. However, due to the popularity of the model, these protocols are being used even 30 to 40 years after their introduction.
Have a look at our blog on Ethical Hacking Tutorial and learn more about these vulnerabilities!
OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model
The OSI model is a legitimate and conceptual design that illustrates the network connection used by systems open to interconnection and communication with other systems. The OSI model is logical and conceptual, defining networking that is utilized by systems that are open to communication and connectivity with other systems.
The OSI model also provides a logical network and efficiently depicts computer packet transport utilizing several layers of protocols.
The OSI model has seven layers:
- Application layer: The application layer interfaces with the top-level of the OSI model application software. This layer is the most user-friendly layer of the OSI model.
- Presentation layer: The presentation layer enables you to establish the form for the data exchange between both interacting bodies. It also assists you in handling the reduction and encryption of data.
- Session layer: This layer regulates the computer dialogues. It helps you to connect the local and remote applications to start-up and end.
- Transport layer: The transport layer builds on the network layer, which transmits data from a process on a source machine to a process on a target machine. It is hosted utilizing individual or multiple networks and supports service quality functions.
- Network layer: The network layer provides functional and procedural methods to transport data sequences of varying lengths from one node to another linked to multiple networks.
- Data link layer: Data link layer corrects physical-layer-capable faults. The layer allows users to set a procedure to join two linked network devices, and it can terminate them.
- Physical layer: The physical layer helps you to describe the data connection’s electrical and physical requirements. This level determines the link between the device and the physical medium of transmission.
The below table depicts the differences between OSI and TCP/IP models:
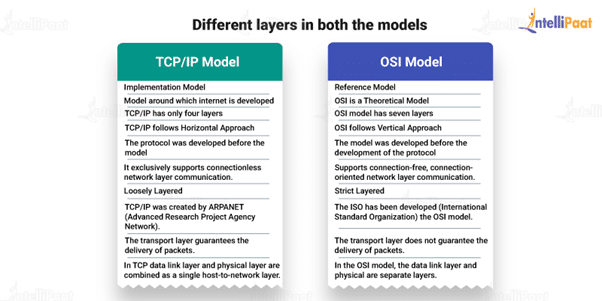
| TCP/IP Model | OSI Model |
| Implementation model | Reference model |
| It is a model around which internet is developed | It is a theoretical model |
| It has only four layers | It has seven layers |
| It follows the horizontal approach | It follows the vertical approach |
| The protocol was developed before the model | The model was developed before the protocol |
| It exclusively supports connectionless network layer communication | It supports connection-free, connection-oriented network layer communication |
| It is loosely layered | It is strictly layered |
| It was created by ARPANET | It was developed by the International Standard Organization (ISO) |
| The transport layer guarantees the delivery of packets | The transport layer does not guarantee the delivery of packets |
| The data link layer and physical layer are combined as a single host-to-network layer | The data link layer and physical layer are separate layers |
Courses you may like
Conclusion
The central aim of TCP/IP was to enable the sending of data packets to one application on a single computer. At first, TCP was designed to meet the data communication needs of the US DoD. TCP/IP is non-relational and, consequently, no firm is controlled by it. This allows the IP suite to be updated easily. It is compatible and can interface with all other operating systems. The IP suite is also fully compatible with the computers and the internet.
Having doubts? Shoot them right away to our Cyber Security Community!
The post What is TCP/IP Model? appeared first on Intellipaat Blog.
Blog: Intellipaat - Blog
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.