What is Spoofing?
Read on to learn how a spoofing attack happens. We will, then, get into its different types and how they can be identified or detected. Finally, we will learn how one can protect themselves against such spoofing attacks.
- What is Spoofing attack?
- Types of Spoofing
- Difference Between Phishing and Spoofing
- Detecting a Spoofing Attack
- How to protect against a Spoofing attack?
- Conclusion
Check out the Cyber Security tutorial offered by Intellipaat.
A spoof usually implies any form of trickery. However, today, when people mention spoofing, it’s mostly in the context of cybercrime. In scenarios where the scammer disguises their identity as another, it’s considered spoofing.
What is Spoofing attack?
Spoofing is a form of cyberattack that occurs when a scammer attempts to gain access to important data or information by disguising themselves as a trusted source. It can happen through emails, texts, phone calls, websites, IP addresses, and servers.
The main goal of spoofing is to gain access to sensitive personal information, bypass network access controls, steal money, or spread malware through infected links or attachments. Spoofers try to steal identities and assets with spoofing via every form of online communication.
Spoofing can occur through a number of different communication channels and different levels of technical know-how. For the spoofing attack to be successful, it has to implement a certain level of social engineering to play on vulnerable human characteristics like fear, greed, and naiveté. Therefore, the methods that cybercriminals use are effective in tricking their targets into giving out their personal information.
Types of Spoofing
Spoofing can take many different forms and there are various types of attacks one should be aware of. Following are the different types of spoofing:
Caller ID Spoofing
A Caller ID allows the receiver of a phone call to know the identity of the caller. When a scammer uses false information to change the caller ID, it is known as Caller ID spoofing. This not only conceals the identity of the scammer but also makes it impossible for the number to be blocked. Occasionally, they use a local area code to make the call seem like a local call.
To create a phone number and caller ID name of choice, scammers use a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol). When the target recipient answers the phone, the scammer will attempt to gain access to important information.
Website Spoofing
In website spoofing, an unsafe website is made to look like a legitimate one by replicating a trusted site. The aim is to take the intended victims to a phishing or malicious site. These sites usually have a similar website address as the original site to easily pass for the real one at first glance. However, they’re more intended to help obtain the visitor’s personal and sensitive information.
Learn Cyber Security from Intellipaat and start your journey.
Email Spoofing
In email spoofing, emails are sent out with fake sender addresses with the intention of infecting a target’s computer with malware, stealing information, or asking for money. The email addresses look legitimate, which convinces the target to open them and click on the malicious link that is usually attached.
The fake addresses are made not too different from the original by using alternative numbers or letters. The ‘from’ field is also sometimes disguised to be the exact email address of someone in the target victim’s network.
Text Message Spoofing
Text message spoofing happens when a scammer sends a text or an SMS using another person’s phone number. This helps scammers conceal their identity behind an alphanumeric sender ID. These malicious text messages usually include links to phishing sites or malware downloads.
IP Spoofing
The objective of an IP spoofing attack is to deceive a computer into thinking that the malicious content being sent to a user is from a trusted source and allow it to pass through. When a scammer wants to hide the location of where they’re sending or requesting data online, they use this method. Some common IP spoofing tools are Netcommander, Sylkie, Aranea, etc.
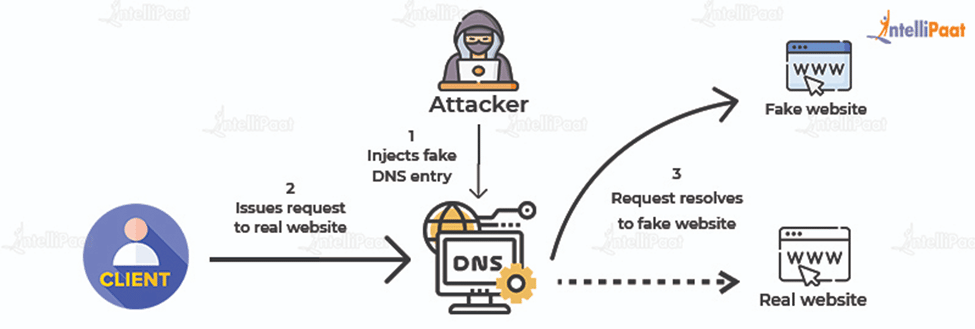
DNS Server Spoofing
Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing reroutes traffic to different IP addresses. Also known as cache poisoning, this type of spoofing leads target victims to malicious websites by replacing the IP addresses that are stored in the DNS server with malicious ones.
The image below shows how DNS spoofing works:

ARP Spoofing
ARP spoofing (Address Resolution Protocol) is often used for in-session hijacking, modifying data, or stealing data. This is achieved by linking the media access control to an IP address. This gives the spammer access to data that was originally meant for the address owner.
GPS Spoofing
When a GPS receiver is deceived by fake signals that resemble real ones, it is known as GPS spoofing. In simple words, the scammer pretends to be located in a place while actually being elsewhere.
Any mobile app that relies on location data from a device could be a target for a GPS spoofing attack. Scammers can use this type of attack to hack a car’s GPS or interfere with the GPS signals of aircraft, ships, buildings, etc.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) Attack
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks happen when a WiFi network is hacked or a duplicate fraudulent WiFi network is created in that location to intercept the web traffic between two parties. Doing so enables scammers to reroute sensitive information like login credentials or credit card information to themselves.
Extension Spoofing
To disguise malware extension folders, extension spoofing is used. This is usually done by renaming the files to “filename.txt.exe” and hiding malware inside the extension. So, the file appears to be a text document when in reality, it runs a malicious program when opened.
Career Transition
Difference Between Phishing and Spoofing
Most phished or spoofed emails are automatically detected as spam. However, it is still important to know the difference between these two popular forms of cyber attack. We have already discussed what spoofing is. Let’s take a look at how phishing attacks take place.
The aim of a phishing attack is to lure a target into revealing personal information, such as login credentials or credit card information. This social engineering technique uses emails that are designed to look legitimate. These legitimate-looking emails trick users into clicking attachments that are potentially laced with malware.
The difference between phishing and spoofing is primarily based on the following parameters.
1. Objective
In phishing, the objective is to extract sensitive personal data of the recipient, whereas, spoofing aims to steal the identity of an individual.
2. Nature of Scam
As surprising as it may sound, spoofing itself is not considered a form of fraud because the attacker does not access the victim’s phone number or email and no data theft occurs. Whereas, phishing involves data theft thus making it an online scam or fraud.
3. Subset
Spoofing is a subset of phishing because attackers may steal the identity of a legitimate user before performing phishing. The other way round is not true.
4. Method
Phishing does not involve malicious software while spoofing does.
5. Types
Phishing types are email phishing, smishing, phone phishing, spear phishing, vishing, clone phishing, etc. Spoofing includes email spoofing, caller ID spoofing, DNS server spoofing, GPS spoofing, IP spoofing, etc.
To appear more legitimate, it is not unpopular for scammers to mix a form of spoofing into their phishing attempts.
Enroll in Intellipaat’s Cyber Security Course and learn from industry experts.
Detecting a Spoofing Attack
If you observe the following indicators, hit delete immediately, click the back button, and close your browser.
In case of email spoofing: –
- The sender’s address doesn’t seem legitimate
- Googling the contents of the email will show if a known phishing email is making the rounds across the web
- Embedded links typically have unusual URLs
- Typos, bad grammar, and unusual syntax in the content of the email
- The email content is too good to be true
- There are attachments from an unknown sender
In case of caller ID spoofing: –
Caller ID is easily spoofed. Landlines have become a hotbed of scam calls, especially, for the susceptible elderly.
In case of website spoofing: –
- There is no lock symbol or green bar near the web address. However, SSL certificates are now free and easy to obtain. While a site may have a padlock, that may not always mean it’s safe.
- The website does not use file encryption HTTPS, especially on a login page
- A password manager that does not autofill login credentials saved in the password vault for a website
Preparing for Cyber Security job interviews? Check out our Cyber Security interview questions now!
How to protect against a Spoofing attack?
The first defense is of course learning how to spot a spoofing attack. Here are several ways one can stay protected against a spoofing attack:
- Turning on the spam filter stops the majority of spoofed emails from ever showing up in the inbox.
- Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments if the email is from an unknown source. If the email seems legitimate, contact the sender through some other channel to confirm.
- In case of suspicion, log in through a separate tab or window. Suspicious emails or text messages request logging in to the account and taking some action. In cases like this, it is advised not to click the provided link. Instead, open the original site directly or log in through the dedicated app.
- Don’t hesitate to call or text the sender if you receive a suspicious email, claiming to be from someone you know, especially if the email or message contains out-of-character requests.
- Show file extensions in Windows to be able to see the spoofed extensions and avoid opening those malicious files.
- Avoid giving out your personal and private information unless you are sure it’s a trusted source.
- Create strong login passwords that are hard to guess and passwords need to be changed frequently. Don’t use the same password for all of your logins.
- Lastly, always invest in a good antivirus program.
Courses you may like
Conclusion
Spoofing attacks on organizations can result in infected computer systems and networks, data breaches, as well as loss of revenue. This leads to a negative impact on the public reputation of an organization. Additionally, spoofing that reroutes internet traffic can overwhelm an organization’s network or lead clients and customers to malicious sites that aim to distribute malware or steal information.
Got questions? Ask our experts in the Cyber Security Community!
The post What is Spoofing? appeared first on Intellipaat Blog.
Blog: Intellipaat - Blog
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.