What is AWS EFS?
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) is a straightforward, serverless, set-and-forget file system. There is no setup or minimum fee. You only pay for the storage you use, for reading and writing access to data kept in Infrequent Access storage classes, and any allocated throughput.
In this blog, we’ll go through the fundamentals of AWS EFS, provide some performance suggestions, and compare it to other AWS storage solutions.
Table of Contents:
- AWS EFS overview
- Amazon EFS features
- AWS EFS Use cases
- Working of AWS EFS
- AWS EFS vs S3 vs EBS
- AWS EFS pricing
- Conclusion
Check out this AWS full course video by Intellipaat
AWS EFS Overview
The AWS Elastic File System (EFS) is one of Amazon’s three primary storage solutions. It is a scalable, cloud-based file system supporting Linux-based applications and workloads that can work in tandem with AWS cloud services and on-premise resources.
Depending on your needs, EFS offers two storage classes: Infrequent Access and Standard Access. Standard access storage is meant for regularly accessed data, whereas Infrequent Access storage is intended for long-term but less frequently used information at a cheaper cost.
The file systems can scale automatically from gigabytes to petabytes of data without the requirement for storage provisioning. An AWS EFS file system can be accessed by tens, hundreds, or even thousands of compute instances at the same time, and Amazon EFS ensures consistent performance for each compute instance.
It is built to be both long-lasting and readily available. There is no minimum price or setup cost with Amazon EFS, and you just pay for what you use.
Amazon EFS features
Amazon EFS comes packed with some great features such as
Fully Managed
AWS EFS is a fully managed service that provides NFS shared file system storage to Linux workloads. It is easy to construct and configure file systems using Amazon EFS. You are not required to manage file servers or storage, update hardware, configure software, or perform backups. Create a fully managed file system in seconds with the AWS Management Console, the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), or an AWS SDK.
Highly available and durable
Amazon EFS is supposed to have a durability of 99.999999999 percent and availability of up to 99.99 percent. For file systems that use Standard storage classes, AWS EFS stores every file system object (that is, a directory, file, and link) redundantly across multiple Availability Zones (AZs). When you choose Amazon EFS One Zone storage classes, your data is stored redundantly within a single AZ.
It is designed to withstand concurrent device failures by detecting and correcting any lost redundancy as rapidly as possible. Furthermore, you can access a file system that uses Standard storage classes from any AZ in the AWS Region where it is situated.
In other words, you can design your application to failover from one AZ to another in the Region for maximum application availability. For all Amazon EFS storage classes, mount targets are meant to be highly accessible within an AZ.
Elastic & Scalable
EFS scales your file system’s storage automatically depending upon the number of documents in your file system. It expands when additional files are added and contracts as ones are discarded. Customers are not required to pre-provision any storage.
EFS can accommodate a petabyte-scale file system, and the file system’s throughput scales with its capacity.
Performance Modes
EFS offers two performance modes:
- General-purpose: General Purpose mode provides the lowest per-operation latency and can accommodate up to 35,000 IOPS. General Purpose performance mode is always used by file systems with EFS One Zone storage classes. You can utilize either the default General Purpose or the Max I/O performance option for file systems with EFS Standard storage types.
- Max I/O: When compared to General Purpose mode, Max I/O mode can support 500,000+ IOPS and has greater per-operation latencies.
Throughput Modes
AWS EFS provides two throughput modes:
- Bursting Throughput: Its default throughput mode is bursting. It is well suited to classical applications with bursty throughput patterns. Bursting Throughput mode saves burst credits by using burst buckets when throughput is low. When throughput is high, burst credits are used.
- Provisioned Throughput: Provisioned Throughput is ideal for applications with a relatively steady throughput. In Provisioned Throughput mode, you define a level of throughput that the file system can drive regardless of the file system’s size or burst credit balance.
Security
The following security measures offered by AWS EFS:
- Network traffic
- File and directory access
- Data encryption
- Identity and Access Management
Career Transition
AWS EFS Use cases
- Simplify DevOps: To boost DevOps agility and respond faster to client input, share code, and other assets in a secure, structured manner.
- Modernize application development: With no management required, you can persist and exchange data from your AWS containers and serverless applications.
- Enhance content management systems: Simplify persistent storage for current content management system (CMS) workloads. Bring your products and services to the market quickly, more reliably, and securely, all while saving money.
- Accelerate data science: It is simple to use and grow, it provides the performance and consistency required for machine learning (ML) and large data analytics applications.
Are you preparing for the AWS interview? Then here are latest AWS interview questions
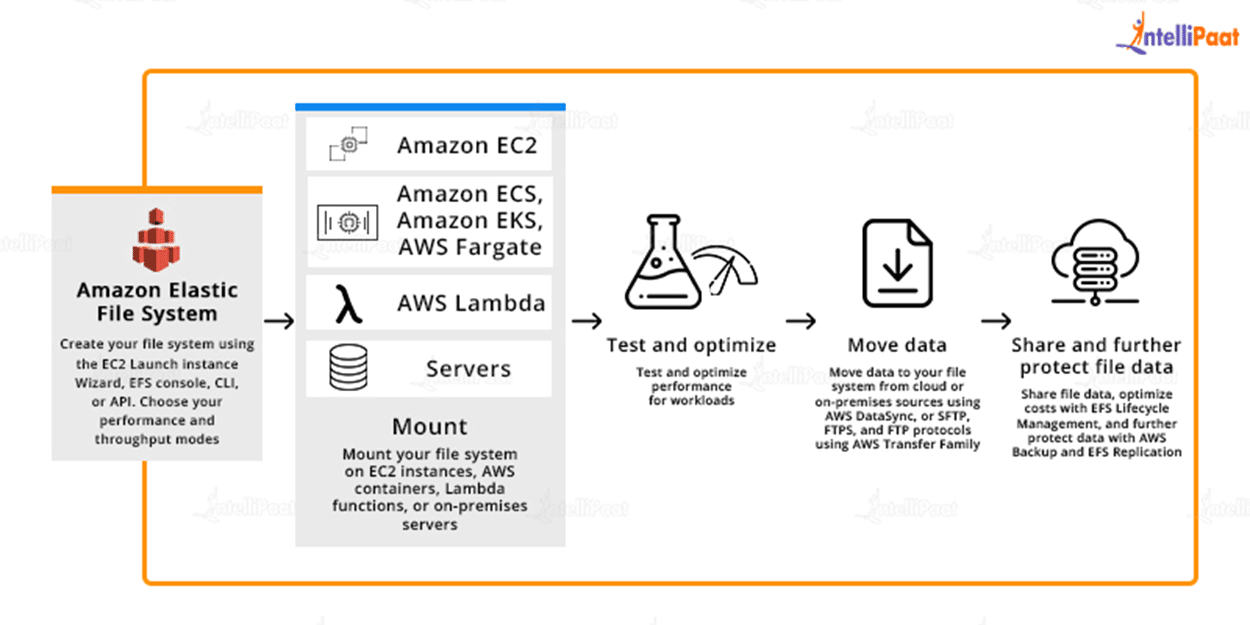
Working of AWS EFS
Amazon Elastic File System dynamically expands and contracts as you add and remove files, with no management or provisioning required.
AWS EFS vs S3 vs EBS
Elastic File Storage (EFS), Elastic Block Storage (EBS), and Simple Storage Service (S3) are 3 different types of storage offered by AWS, and they all have their advantages.
Let’s compare them to get a better idea of what kind of storage suffices your needs.
| AWS EFS | AWS S3 | AWS EBS | |
| Performance | 3GB/s baseline performanceUp to 10GB/s throughputUp To 500k IOPS | Supports 3500 PUT/LIST/DELETE requests per secondScaleable to 5500 GET requests per second | HDD Volumes 250-500 IOPS/volume depending on volume typeSSD volumes 16-64K IOPS/volume |
| Availability and Accessibility | No publicly available SLAUp to 1000 concurrent instancesAccessible from any AZ or region | Usually 99.9% availableIf lower, returns 10-100% of the costAccessible via the Internet using APIs | 99.9% available Accessible via single EC2 instance |
| Access Control | IAM user-based authenticationSecurity groups | Acess is based on IAMUses bucket policies and user policiesPublic access via Block Public Access | Security groupsUser-based authentication (IAM) |
| Storage and File Size Limits | 16TB per volume52TB maximum for individual files | No limit on the quantity of objectsIndividual objects up to 5TB | Max storage size of 16TBNo file size limit on disk |
| Cost | Standard storage: $0.30-$0.39 per GB-month depending on regionInfrequent storage: $0.025-$0.03 per GB-monthProvisioned throughput: $6 per MB/s-month | Free tier: 5GBFirst 50 TB/month: $0.023 per GBNext 450 TB/month: $0.022 per GBOver 500 Tb/month: $0.021 per GB | Free tier: 30GBGeneral Purpose: $0.045 per GB/monthProvisioned SSD: $0.125 per GB/month, $0.065 per IOPS/month |
The advantage of using AWS EFS over AWS EBS is that EFS, unlike EBS, may be mounted by many EC2 instances, which means that many virtual machines can store data within an EFS instance.
Check out Intellipaat’s AWS Training Course to get ahead in your career!
Amazon EFS pricing
You only pay for the resources you use with Amazon EFS. There is no minimum price and no setup fees. It has two storage classes: standard storage and infrequent access storage, which is cost-effective for data that aren’t accessed every day.
- Amazon EFS Standard Storage Class (Default): The Standard storage class is intended for active file system workloads, and you only pay for the file system storage you use per month.
- AWS EFS Infrequent Access Storage Class: For files that are viewed rarely, the Infrequent Access storage type is cost-effective. Data saved on the Infrequent Access storage class is less expensive than Standard, but you must pay a price each time you read or write to a file.
- Amazon EFS Bursting Throughput (Default): There are no charges for bandwidth or requests in the default Bursting Throughput mode, and you receive a baseline rate of 50 KB/s per GB of throughput included within the storage price.
- AWS EFS Provisioned Throughput: You can choose the Provisioned Throughput mode to provision your file system’s throughput independent of the amount of data stored and pay for storage and throughput separately. The Provisioned Throughput mode, like the normal Bursting Throughput mode, provides 50 KB/s per GB (or 1 MB/s for 20 GB) of throughput in the price of storage. You are only charged for the additional throughput delivered above what is provided based on the data you have stored.
Courses you may like
Conclusion
Amazon EFS is one of Amazon’s primary storage offerings. Once you grasp the fundamental concepts of AWS EFS, you may optimize your application’s speed while also lowering its cost.
If you want to dive deeper into AWS then do check out our AWS Master Certification.
The post What is AWS EFS? appeared first on Intellipaat Blog.
Blog: Intellipaat - Blog
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.