How Do Electric Cars Work?
What is Electric Car?
An Electric Car (EV) is essentially an automated vehicle powered by an electric motor. An electric vehicle does not use or have a gasoline or diesel engine. When you put an electric automobile in ‘drive,’ it accelerates much like an automatic vehicle. Electric and hybrid vehicles have no gears. They are all fully automated vehicles.
For getting an overview of the Electric Vehicle Course, Watch this course introductory video
Table of Contents
- Key Components of an Electric Car
- Working of an Electric Car
- Working of an Electric Car Engine
- Charging System of an Electric Car
- Benefits of an Electric Car
- Conclusion
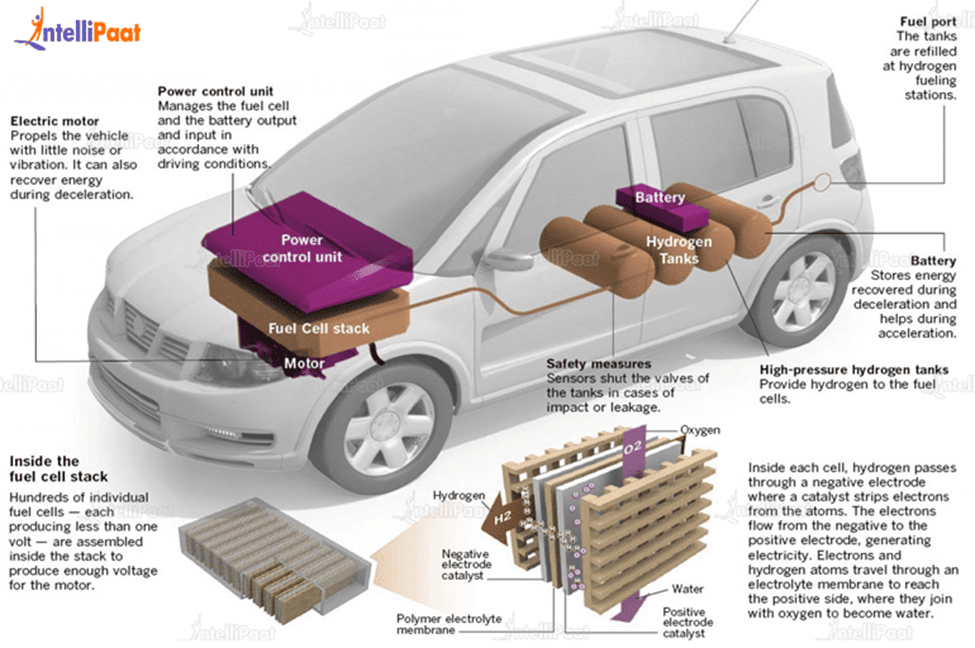
Key Components of an Electric Car

- Battery (all-electric auxiliary): The auxiliary battery is used to operate the accessories of the vehicle
- Onboard charger: This device connects the charging accessories and examines the battery parameters like current, temperature, and voltage.
- Power electronics controller: The power electronics controller is used to manage the speed and torque produced by the traction motor.
- DC/DC converter: The dc-dc converter is used to coverts the higher voltage direct current from the battery pack to the lower direct current and this power is used to engage the vehicle accessories.
- Electric traction motor: This motor gets its power from the traction battery pack to power the vehicle’s wheels.
- Charge port: The charger port is the external power source for the electric Vehicle
- Thermal system (cooling): The thermal system keeps the temperature range in the safe zone for accessories like electric motors, engines, and other components.
- Traction battery pack: It stores the energy released by the traction motor.
Working of an Electric Car
Electric cars operate by connecting to a charging station and drawing power from the grid. The electricity is stored in rechargeable batteries and used to power an electric motor, which drives the wheels.
Compared to conventional gasoline-powered vehicles, electric vehicles accelerate more quickly, giving the impression that they are easier to operate.
The electric motor receives energy when you push the accelerator, moving it from the battery. The drive shafts spin the wheels when the motor is energized. When you use the brakes, the vehicle begins to decelerate and the motor converts into an alternator, producing power. The battery receives this energy back after that.
Want to learn about Electric Vehicles from the Experts, here’s a golden opportunity for you Intellipaat’s Electric Vehicle Course!
Working of an Electric Car Engine
The electric engine of an EV does not need to pressurize and burn gasoline to drive the car’s wheels. Instead, it generates rotational force by using electromagnets inside the motor that are driven by a battery.
There are two sets of magnets within the motor. One pair is linked to the shaft that spins the wheels of the automobile, while the other is contained within the housing that surrounds that shaft.
The two sets of magnets are charged in such a way that their polarities are opposite, and they repel one another. The force of the magnets pulling apart rotates the shaft, spins the wheels, and propels the vehicle forward.
To maintain a consistent state of repulsion between the magnets, their polarity must vary as the shaft rotates. Otherwise, they’d gradually rotate back to a position where they’d attract rather than repel each other, locking themselves in place.
This is done automatically by switching between positive and negative voltage. However, because the electricity from an EV’s battery is direct current (DC), an inverter is required to continually switch the polarity of the magnets.
To maintain rotational force, an EV’s inverter reverses polarity at a rate of roughly 60 times per second.
A separate DC converter(Which opens in a new window) is utilized to direct power to other car systems that do not need alternating current (heating, infotainment, and lighting).
The driver can change the frequency of the current supplied to the motor, and the higher the frequency, the more frequently the polarity switches. This generates more rotational force, or torque, causing the wheels to spin faster.
Charging System of an Electric Car
With gas-powered vehicles, you fill-up the tank and drive away. There are now three charging stations available for EVs, ranging from the slowest (level 1) to the quickest (level 3).

- Level 1: These chargers are standard 120-volt wall connections that are best used in private houses where you can charge overnight. It moves slowly: An 8-hour charge adds around 40 miles to the range; a full charge could take 20 hours or more.
- Level 2: Level 2 stations step up to 240 volts and produce 10-25kW for a complete charge in around eight hours. As a result, they are the most prevalent method for overnight charging at home or in places such as hotels.
The Destination Chargers are Tesla Level 2 stations (versus Superchargers). If you don’t have a suitable socket, you’ll need to install a 240-volt outlet or a home charging station to recharge an EV at home.
- Level 3: Level 3 DC fast charging (DCFC) stations provide the highest power, it charges an EV battery up to 80% in around 30 minutes.
They provide an average of 50kW, while some, such as Tesla’s Superchargers, provide substantially more power to the battery.
The majority of EVs are equipped with a power chord that can be plugged into level 1 and level 2 charging stations, which are the two most prevalent charging levels available.
Teslas also have an adaptor that can be used at non-Tesla charging stations (mobile chargers are no longer bundled). The majority of public charging stations will include several connection connectors that provide level 2 and 3 electricity.
Benefits of an Electric Car

- Less expensive operations:
Comparable gasoline or diesel vehicles have far higher operational expenses than electric automobiles. Electric vehicles use energy to recharge their batteries rather than fossil fuels like gasoline or diesel.
- Low maintenance cost:
Electric automobiles require less maintenance than internal combustion vehicles since they have fewer moving components.
Vehicles driven by traditional gasoline or diesel engines require more maintenance than electric cars. As a result, running an electric automobile has substantially reduced yearly operating costs.
- No noise pollution:
Due to the absence of an engine, the noise will not exist.
- Tax and financial advantages:
Compared to gasoline or diesel cars, electric car registration and road tax are less expensive. Depending on which state you live in, the government provides a broad range of guidelines and incentives.
Career Transition
Conclusion
From the introduction of the first electric vehicle in 1837 to the present, there have been significant advancements in technology as well as in people’s perceptions of the effects of automobiles on the environment and other mobility options.
Although the electric vehicle sector is now a profitable target for Indian corporations and start-ups, numerous challenges must be overcome before EVs are ready for broad adoption. For instance, producing electric vehicles locally is a high-cost barrier.
Your doubts get resolved on Intellipaat’s community Page!!
The post How Do Electric Cars Work? appeared first on Intellipaat Blog.
Blog: Intellipaat - Blog
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.