Cassandra Data Modeling
In this blog, we will evaluate the various key concepts of data modeling in Cassandra and how to approach those.
Cassandra is an Apache-distributed database that is highly scalable and made to handle extremely large volumes of structured data.
Today, we’ll learn about what Cassandra data modeling is, why developers choose Cassandra, and its architecture. In addition to that, we will also discuss the pros and cons of this technology.
Points at a Glance
- What is Data Modeling?
- What is Cassandra Data Modeling?
- Cassandra Architecture
- Advantages of Cassandra Data Modeling
- Drawbacks of Cassandra Data Modeling
- Conclusion
Watch this video to gain an understanding of all the concepts of Apache Cassandra, in detail.
Before getting into the details of Cassandra Data Modeling, let us first see what exactly data modeling is anyway.
What is Data Modeling?
Data modeling is the act of developing a graphical representation of an entire information system or certain components of it, in order to convey relationships between various data points and organizational structures. The objective is to explain the various forms of data that are used and stored within the system, the connections between different categories of data, the various ways that data can be categorized and organized, as well as its formats and features.
Standardized schemas and formal methodologies are used in data modeling. This gives everyone in an organization—or even outside of it—a common, predictable approach to defining and managing data resources.
Great! So now we are aware of the meaning of Data Modeling. It’s time to get started with the main part of the blog and understand Cassandra Data Modeling in-depth.
What is Cassandra Data Modeling?
Apache Cassandra is a distributed (or decentralized), open-source database. It is a type of non-relational (NoSQL) database that is consistent and highly scalable.
Some of Cassandra’s significant features are given below:
- Cassandra data modeling was launched in July 2008.
- Data modeling in Cassandra is query-driven.
- It stores data in the form of tables. Each table consists of its own rows and columns.
- To query the data in the tables, CQL or Cassandra Query Language is used.
- Because it is a NoSQL database, Cassandra is schema-free and allows easy replication of data.
- Cassandra is fault-tolerant.
- It follows the column-oriented database model.
- It was first created by Facebook for its inbox search and then made open-source.
- Many organizations such as Netflix, Twitter, and Facebook make use of Cassandra data modeling.
To help you understand Cassandra in a better way, here is a brief description of its architecture.
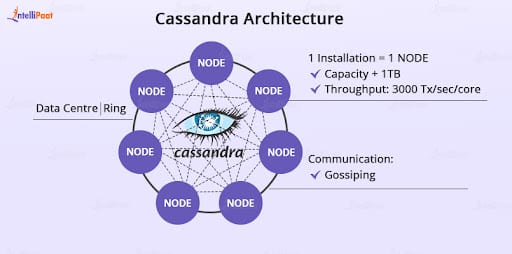
Cassandra Architecture

In Cassandra data modeling, the data is distributed among nodes in clusters. Its main aim is to manage huge amounts of data with no single point of failure.
- All the nodes in the Cassandra architecture, although interconnected, are independent of each other.
- Each one of these nodes in Cassandra can play the same role and perform all the database operations, without the need for a master node.
- No matter where the data is present in the cluster, each node in the cluster can accept read and write data requests.
- Read and write requests can be easily served by other nodes in the cluster, in case of failure of a node.
Data Replication Strategy
This strategy is used to ensure that there is no single point of failure. To attain higher durability and availability, Cassandra makes use of replication. Here, one or more nodes act as replicas.
There are two types of replication strategies:
- Simple Strategy
- Network Topology Strategy
It follows the ring-type architecture and consists of multiple data nodes and centers. In addition, it does not have any master nodes.
Enjoying learning about Cassandra Data Modeling? Take this Cassandra course to learn all the necessary concepts related to Cassandra from experienced professionals!
Advantages of Cassandra Data Modeling

Here are a few advantages of Cassandra Data Modeling to aid you in understanding the concept better:-
Scalability
High scalability is one of the most important advantages of Cassandra Data Modeling. Owing to its distributed architecture, Cassandra supports both elastic and linear scalability. The clusters in Cassandra can be easily modified to scale up or down. The user doesn’t need to change the queries or restart a cluster in order to add or delete nodes in it. This is what makes Cassandra have an extremely high throughput.
Availability and Fault Tolerance
The data replication feature of Cassandra makes it possible to be highly available and fault tolerant. Moreover, as we have already discussed, all nodes in Cassandra are equal. Due to this, even if multiple nodes fail at the same time, the overall availability won’t be affected.
Performance
High performance is a notable benefit of Cassandra. Being a NoSQL database, Cassandra, like many other NoSQL databases, provides great performance features. It has a high throughput and minimum latency issues. It also has great speed as compared to several other alternatives.
Architecture
We have already covered Cassandra’s architectural model in the blog above. We discussed some unique features, such as:
- Cassandra database model is open-source and schema-free.
- It supports peer-to-peer instead of a master-slave architecture, without any single point of failure.
- Any server has the ability to take requests from any client because all nodes are equal in the cluster.
These features help in making the Cassandra database robust, flexible, and highly popular.
Every technology, with its wonderful features and unique benefits, also has its own disadvantages. So does Cassandra!
Drawbacks of Cassandra Data Modeling
Here we’ll look into some of the cons of Cassandra Data Modeling:-
- It does not offer subquery or join support.
- It does not support aggregate, ACID properties and other relational database properties.
- Users need to search for Cassandra among other third-party companies and websites because it is not yet officially documented by Apache.
- We already know that Cassandra can handle large amounts of data. But this has a disadvantage of its own. Because of managing huge amounts of requests and data, the transaction speed in the database decreases. As a result, the users can face latency issues.
- The same piece of information in the case of the Cassandra database is stored multiple times. This is due to the fact that data in Cassandra is modeled around queries instead of a structure.
- The column value in the database cannot exceed 2GB. Consequently, 64GB is the limit of collection value.
Here is a list of the most popular Cassandra interview questions along with their answers, to help you ace your next interview!
Conclusion
Cassandra is a great tool for developers and especially for organizations that have huge quantities of data to manage. Its amazing features and architecture make it the right choice for a lot of businesses. However, before deciding to choose this specific database model, it is necessary to look at its limitations as well. Nevertheless, Cassandra is an emerging technology and considering its notable characteristics, it is safe to say that it will be here for a long time.
Have doubts related to the topic? Drop your queries here on our Community Page!
The post Cassandra Data Modeling appeared first on Intellipaat Blog.
Blog: Intellipaat - Blog
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.