Blockchain and Capgemini SAP Leonardo – Part 1
Blog: Capgemini CTO Blog
1 Introduction
Building upon the blog series on “Turning digital aspirations into reality with SAP Leonardo and Capgemini,” we will be looking at how SAP Leonardo, together with Blockchain, can be leveraged to collaborate and optimise processes with security and transparency.
Firstly, we look at the business challenges faced by various Lines of Business for example Supply Chain Management and lack of traceability or Aftermarket and counterfeit parts. Blockchain is a technology with the potential, for the right applications, to have a big impact on business processes.
Secondly, we look at understanding blockchain as an enabling technology for sharing and trusting data across multiple parties. In blockchain terminology this is a capability for open integration, permissioned, trustworthy and transparent business processes.
Capgemini are co-innovating with SAP and customers to begin and expand their SAP Leonardo Blockchain journey. SAP Leonardo is delivering capabilities to create and scale new intelligence applications. SAP Leonardo represents a range of technologies including Internet of Things, Machine Learning, Analytics, Big Data, Data Intelligence and Blockchain; technologies that when combined have a greater capability than individually.
This blog is focussing on SAP Leonardo Blockchain as a foundation for building transactional applications that establishes trust and transparency while streamlining business processes. Part two of this blog continues the discussion about blockchain use cases.
Key terms: Blockchain, SAP Leonardo, Distributed Ledger, Smart Contract
2 The Blockchain Business Case Challenge
An effective place to start is with the business problem. Identifying the issue or process and applying an approach for effective problem solving; drawing on a cross section of skills and knowledge to accelerate the process. Fast Digital for Discrete Manufacturing, Agile methodolgies and Capgemini’s Applied Innovation Exchange network are resources for effective transformation and specifically, to stay on subject with this blog, determining if, where and how blockchain innovations can add value.
Blockchain is applicable and can add value where one or more of the following are present, see Figure 1. The exact justification should be reflective of the actual business problem in full context, this is part of the journey when developing a business case.
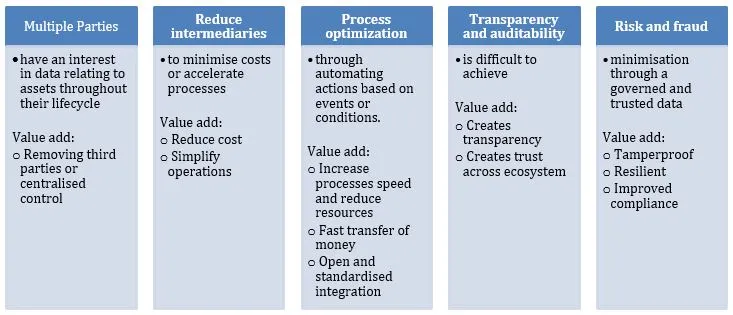
Figure 1 Process Value Add
Potential applications are varied ranging from traceability of assets, payments, connecting products through to proving provenance. The next step is to explore how connecting blockchain to technologies such as IoT can automate tasks, combine multiple processes and improve processes. This is where it really starts to get interesting.
Blockchain has several inherent features that can address real challenges; the type of blockchain also influences the features as discussed in section 3. Traceability across the supply chain can benefit from the distributed ledger and being an immutable system of record. In a similar manner challenges such as counterfeiting can be address using an accessible ledger and single source of truth. Efficiency and speed can increase through blockchains capability for peer to peer transactions and automation, whether this is the transfer of value or authentication.
As an initial focus area Capgemini are currently designing and building PoC applications in Purchase to Pay (P2P), Maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) and Supply Chain. The challenge is transforming and not merely using the latest technology, linking processes and assets with the flow of data; part two of this blog continues the discussion on blockchain use cases.
3 What is Blockchain?
If we start by defining what blockchain is not. It is not a single solution, model or application, this is like defining IoT devices as only measuring temperature. Blockchain is also not a standalone solution, it will be an integral component connecting all systems; integrating the speed, agility and power of existing Systems or Record (E.g. ECC or S/4 Hana) with the innovations of SAP Leonardo.
Originally deployed as a technology to trade digital currency Bitcoin in 2008, blockchain has potential far beyond just supporting cryptocurrency. Blockchain is the term for the underlying technology behind Bitcoin and other applications.
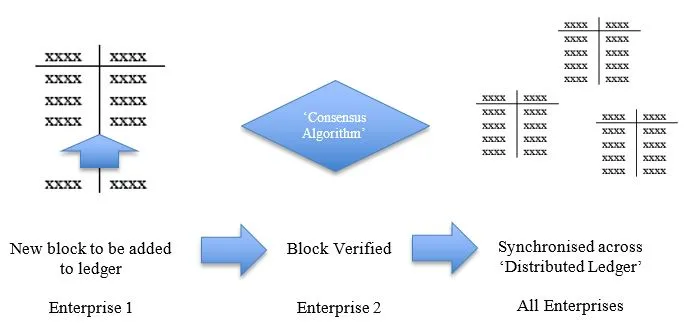
Figure 2 Simple Overview
Blockchain is based on a distributed ledger, a database of transactions that is shared and synchronised across multiple computers and locations, see Figure 2. Think of any transaction such as an asset changing hands from organisation to organisation in a supply chain. Each transaction is recorded in a block in a blockchain, a peer to peer transaction with no intermediary. The supply chain has many participants that can all view and verify the data to determine whether to accept or reject the transaction. If the transaction is verified it is added chronologically as a block to the blockchain. The blockchain is propagated to the distributed ledger (copies are held by each participant), secured through cryptography and accessed by keys to encrypt and decrypt the data. Every participant can read the data if they have permission and dependant on the type of blockchain.
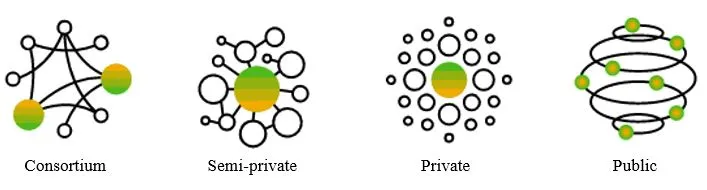
Figure 3 Blockchain Types
There are many types of blockchain, tailored to suit the processes they support, see Figure 3. Consortium is currently the most accepted for Enterprises (SAP, 2017) where the participants are a defined group. This is permissioned and very applicable for business. Other variations range from private to public with permutations between the extremes.
A useful capability of blockchains is “smart contracts”. These are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions. They may be triggered from the real world such as sensor as part of IoT or as an outcome of a transaction, for example, a change ownership. To be successful blockchain solutions must support business processes across companies and industries in a heterogeneous landscape.
The final point is that blockchains are searchable, another powerful argument for blockchains. Ultimately blockchain is stored in a database accessible by a wide range of familiar tools. Data storage is different, the whole blockchain is stored, including data generated outside the boundaries of an individual Enterprise.
Capgemini are co-innovating with SAP and customers to begin and expand their SAP Leonardo Blockchain journey. SAP offers Blockchain services via SAP Cloud Platform. As part of SAP Leonard this brings to together a range of capabilities including Internet of Things and Machine Learning with blockchain in a single environment; technologies that when combined have a greater capability than individually.
In this blog we discussed the challenges and benefits of blockchain technology and SAP Leonardo. Blockchain is a technology with the potential, for the right applications, to have a big impact on industry. The challenge is identifying the right application and developing the business case. Part two of this blog continues the discussion about blockchain use cases.
This is part of the blog series entitled “Capgemini’s Fast Digital with SAP Leonardo.” Other blogs are:
Blog 1: Turning digital aspirations into reality with SAP Leonardo and Capgemini
Blog 2: SAP Leonardo—Increasing Supply Chain Visibility
Blog 3: Designing to Deliver—How Capgemini uses Design Thinking and SAP Leonardo
Blog 4: Lone worker and connected devices with SAP Leonardo
Blog 5: Minimising production downtime with predictive maintenance
Blog 6: “Voice”—the new UI for the enterprise
Find more information on the Capgemini Leonardo Services website. Contact one of our experts today to discuss.
By Martin Watmough & Mark Williams