What Is Hyper-Automation?
Blog: ProcessMaker Blog
The term “hyperautomation” appeared in October of 2019, taking the top spot on Gartner’s Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2020 list. Yet the concept of hyperautomation is also encompassed within other industry terms. For instance, Forrester refers to it as “digital process automation,” while IDC and others use “intelligent process automation.”
Regardless of which term is used, hyperautomation is a powerful set of digital technologies that will continue to transform organizations across nearly every industry. In this article, we will explore what hyperautomation is, the digital technologies that it consists of, and the many benefits that it offers.
What is hyperautomation?
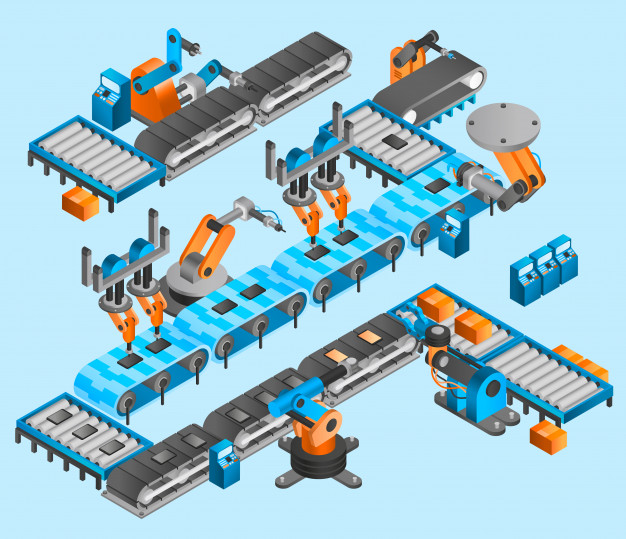
Hyperautomation refers to the use of advanced technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA), to automate tasks that were once completed by humans. Hyperautomation not only refers to the tasks and processes that can be automated, but also the level of automation. It is often referred to as the next major phase of digital transformation.
It is important to note that hyperautomation is not meant to entirely replace humans. Rather, through automation, humans are freed from repetitive and low-value tasks to focus on ones that are of a higher-value to the organization. Together, automation and human involvement helps organizations to provide superior customer experiences while reducing operational costs and boosting profitability.
The ability to include humans in the digitization process is a key component of hyperautomation. The first wave of automation technologies largely relied on robotic process automation (RPA). RPA involves the use of bots to mimic repetitive human tasks. These processes are rule-based and utilize structured data to complete actions. Unlike artificial intelligence which seeks to simulate the human intellect, RPA focuses solely on human actions. With hyperautomation, digital workers operate alongside humans to deliver unmatched efficiency.
By using a combination of automation technologies, hyperautomation can overcome some of the limitations of approaches that rely on a single automation tool. This allows organizations to move beyond the confines of individual processes and automate nearly any tedious and scalable task. Automation, however, requires careful planning and implementation. Organizations need to understand how digital technologies will fit into their existing workflows, as well as what roles they will play in new processes. Simply introducing automation into a business process without appreciating the role that it will play, or automating a process that is already broken, can have major consequences at the organizational level.
Another major attribute for hyperautomation is integration. To achieve scalability in operations, various automation technologies must work together seamlessly. Careful planning, implementation, and improvement of processes is accomplished through intelligent business process management (BPM). For these reasons, BPM is a core component of hyperautomation.
The key components of hyperautomation
There are several automation technologies that comprise hyperautomation. These include:
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
- Business process management (BPM)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and/or Machine learning (ML)
- Advanced analytics
Robotic process automation
Robotic process automation leverages technology like software bots to replicate repetitive human tasks. RPA typically works for tasks that are rule-based, have defined inputs and outputs, are repeatable, and occur often. One limitation of RPA is that it is limited to structured data to complete tasks. Thus, RPA does not have the ability to understand context or learn, nor can it access and make sense of unstructured data sources like images.
Business process management
BPM is one of the most important components of hyperautomation. In many ways it is the foundation on which any successful automation strategy is built, monitored, and improved. Introducing different digital tools into business processes, especially for those organizations new to automation, can be challenging.
Organizations must create new workflows and test them prior to deploying them to avoid breakdowns that can have disastrous consequences for their businesses. Business process management software is a powerful and simple tool that can be used to manage an organization’s hyperautomation strategies and initiatives.
Artificial intelligence and/or machine learning
AI is a method of making computers operate in ways that simulate human intelligence. Organizations use AI to carry out specific tasks without being explicitly programmed to do so. Common examples of AI are virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa and marketing technologies that suggest products you may be interested based on past behavior.
ML, often used synonymously with AI, is a branch of AI that uses computer algorithms to allow systems to automatically improve over time. Organizations use both supervised and unsupervised algorithms to identify patterns in data. Supervised algorithms create inputs and outputs before making predictions on their own. Unsupervised algorithms observe structured data and develop insights from pattern recognition.
AI and ML are powerful automation tools. Yet implementing them can require a significant investment of resources and careful planning to ensure integration with other technologies and processes. For these reasons, achieving hyperautomation requires the strategic deployment of AI and ML.
Advanced analytics
Hyperautomation offers organizations powerful analytical tools and capabilities. Hyperautomation overcomes the data limitations of relying on a single automation tool like RPA. While RPA is limited to structured data, hyperautomation technologies can handle both structured and unstructured data. This helps organizations to access and analyze data that has traditionally been inaccessible to gain important organizational level insights.
Hyperautomation can also convert unstructured data into structured data for use with RPA technologies. This relationship is an illustration of how various digital tools work together seamlessly to offer unmatched efficiency.
Benefits of hyperautomation
Hyperautomation offers many benefits and potentially unlimited upside. Some major benefits of hyperautomation include:
- Flexibility. Since hyperautomation relies on a multitude of automation technologies, organizations can move past the limited benefits of a single digital technology. This helps organizations to achieve scale and flexibility in operations.
- Improved employee productivity. By automating time consuming tasks, employees are able to get more done with less resources and serve more valuable roles in organizations.
- Integration. With hyperautomation, organizations can integrate digital technologies across their processes and legacy systems. Stakeholders have better access to data and can communicate seamlessly throughout the organization.
- Improved ROI. Hyperautomation boosts revenue and reduces costs. With powerful analytical tools and capabilities, organizations can optimize the deployment of their resources.
About ProcessMaker
ProcessMaker is a low-code business process management software. ProcessMaker is relentless about helping organizations around the globe achieve operational efficiency through hyperautomation technologies. Headquartered in Durham, North Carolina in the United States, ProcessMaker has a partner network spread across 35 countries on five continents. Hundreds of commercial customers, including many Fortune 100 companies, rely on ProcessMaker to digitally transform their core business processes enabling faster decision making, improved compliance, and better performance.
The post What Is Hyper-Automation? appeared first on ProcessMaker.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.