Technology and business trends for 2021
Blog: AuraQuantic Blog
Like every year, Gartner has published its annual report with its forecasts on what will be the most influential technology and business trends in 2021.
According to the consultancy firm, next year will continue to be marked by the COVID 19 pandemic, and companies will have to continue working in a volatile, unknown and difficult to predict environment. Therefore, they will need technologies that give them flexibility and adaptability, empowering people as the center of all businesses regardless of their physical location.
“The need for operational resiliency across enterprise functions has never been greater”
The pandemic crisis has left businesses in a delicate situation, and is forcing them to rethink their operational strategies in order to strengthen their resilience and better cope with any future crisis.
In its annual report, Gartner suggests that organizations have already overcome the first impact of the pandemic, and are moving from a reactive to a proactive strategy, they should focus on these three areas: People Centricity, Location Independence and Resilient Delivery.
People Centricity
The pandemic has changed the way people work and interact with organizations, but people remain at the center of all businesses and need digitized processes to carry out their activities.
Gartner identifies three technologies that can help companies remain focused on the people.

Internet of behavior (IoB)
The goal, of the Internet of behavior, is to identify habits or behaviors to influence people’s decisions or behaviors.
To achieve this, IoB uses data from different sources such as: Internet, facial recognition, location tracking, physical activity monitoring, biometric parameters, actions in social networks, consumption analysis and purchase habits, etc.
Obviously, this technology has important social and ethical implications, and its social acceptance will largely depend on the use that organizations make of it.
For example, everyone would agree to give up their driving data if they were to benefit from it, but no one would agree to share this data with the police.
IoB brings many advantages to companies and individuals, but it also poses a risk that ethics and legal regulation must harmonize.
Towards a ‘total experience’
Traditionally, multi-experience, user, customer and employee experiences have been treated separately. However, now Gartner goes a step further and indicates that they must connect to evolve and give a better experience to all parties.
According to the consultancy firm, since companies are trying to optimize all experiences, this combination can offer an excellent opportunity to differentiate themselves from the competition.
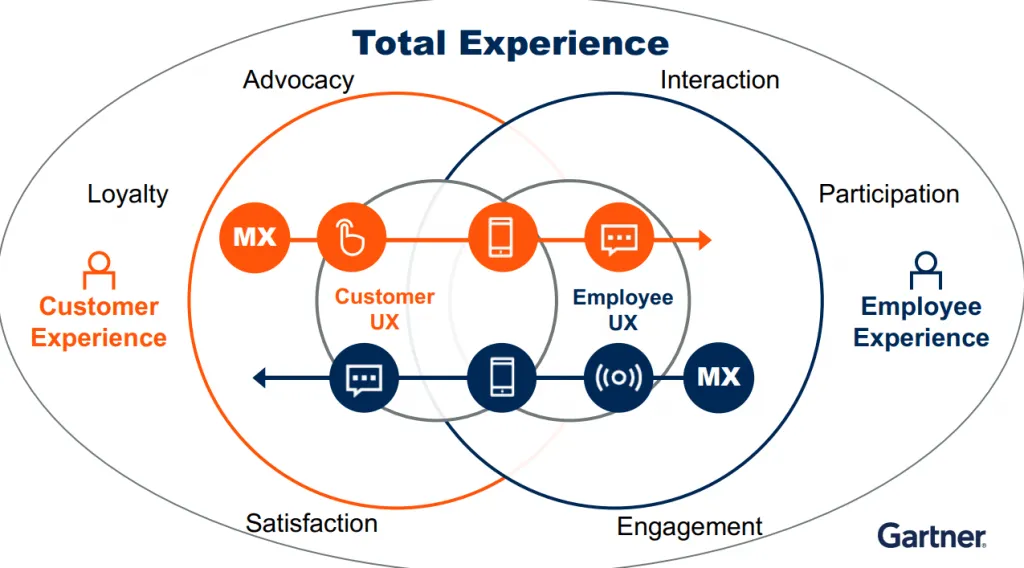
As interactions become more mobile, virtual, and distributed, a total experience strategy that satisfies customers, employees, and users alike becomes more necessary.
To achieve this goal, it makes sense to focus on an improvement strategy that is useful to all groups.
Privacy-enhancing computation
Data privacy has become a critical issue in recent years and more and more regulations are being added to force organizations to focus on this issue.
Today, options such as remote work are part of the corporate culture, but nevertheless access from outside the corporate network can compromise the security of the data.
Therefore, it is necessary to use data protection technologies that also guarantee security, privacy and anonymity.
Gartner highlights three technologies aimed at improving privacy:
- The first provides a trusted environment to process or analyze sensitive data. It includes trusted third parties and trusted hardware-based execution environments (Confidential Computing) that protect data while it is in use.
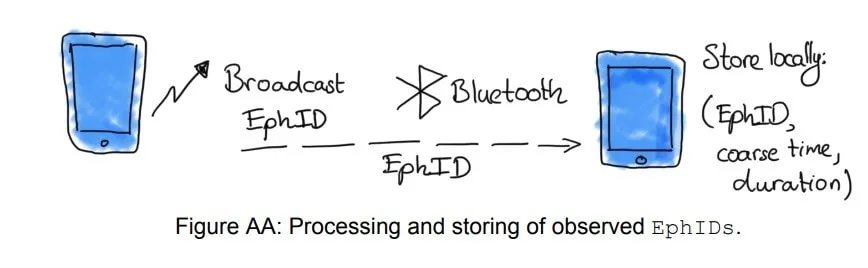
- The second performs the processing and analysis in a decentralized way (example COVID 19: tracking system and coincidence analysis carried out on the device) with the aim of anonymizing the data before it is processed. It includes Federate Machine Learning and Privacy-aware Machine Learning models that enable training models without transferring potentially sensitive user data from devices, or local deployments, to a central server.
- And the third transforms data and algorithms before they are processed or analyzed. It includes the following technologies:
- Differential privacy: allows you to collect and share data, mathematically guaranteeing that the privacy of each person will be maintained.
- Homomorphic encryption: the data is sent encrypted and a code is provided so that operations are carried out on the data without decrypting it to later return it encrypted to the sender.
- Secure Multiparty Computing (MPC / SMPC): It is a cryptographic protocol so that data can be calculated between multiple parties without any individual party being able to see the data of the other parties.
- Zero knowledge proofs: it is a cryptographic method by which one of the parties can demonstrate to the other the veracity of information, without revealing sensitive information about said information.
- Private set intersection: it is a cryptographic technique that allows two parties to compare data sets without giving up the privacy of their individual data. In other words, PSI (Private set intersection) allows you to test if the parts share a common data point (location, identification, etc.).
- Private information retrieval: it is a protocol that allows to recover an element from a database without the owner being able to determine which one.
Organizations have discovered the potential of their data, but at the same time, new laws are emerging in all countries to protect the privacy of their citizens. For this reason, companies must adapt their data analysis and processing technologies and their security controls to guarantee privacy.
LOCATION INDEPENDENCE
The COVID 19 pandemic has given the definitive boost to remote work, and organizations around the world have had to adapt their organization, and introduce technological improvements, to adapt to the new times.
Distributed cloud
Unlike the highly centralized public cloud (Cloud), a distributed network offers its services from different physical locations, maintaining the operation, governance and evolution of these services, under the responsibility of the public cloud provider.
The objective of this type of cloud is to bring the location of computing resources closer to the place where data and business activities are produced, reducing latency and improving response times.
This type of cloud also solves scenarios where the law of a country or area, such as the European Union, has specific regulations that prevent the data from traveling outside the user’s country of origin.
On the other hand, customers can benefit from the advantages of a public cloud, but without the high costs and complicated solutions that a private network implies.
These are some of the distributed cloud modalities:
- On-premises public cloud: It is composed of cloud computing resources that are exclusively used by a company or organization. It can be hosted in the local data center or with an external service provider.
- Internet of Things (IoT) edge cloud – A distributed cloud substation designed to directly interact with or allow edge devices to host public cloud services. It includes industrial and consumer IoT capabilities, and supports use cases such as collection, broadcast, and movement. As with the local public cloud, these resources can be restricted in access and visible to a single company if necessary.
- Metropolitan Area Community Cloud: Cloud substations with local capabilities for a city or metropolitan area.
- 5G mobile edge cloud: a cloud substation distributed in a 5G telecommunications operator network with the aim of bringing service provision closer to the edge of the network and obtaining responses in near real time.
- Global Network Edge Cloud – Distributed cloud substations designed to integrate with the global network infrastructure. A connected car will incorporate cameras and sensors that will provide information about the environment in real time and will generate about 25 GB per hour and approximately 300 TB of data per year. That information will need to be processed, but moving that amount of data between the servers and the car is unaffordable, so the processing needs to occur much closer to where the data is being generated, at the edge of the network ( mobile phone towers, hubs, routers, smartphones, etc.).
Interest in hybrid cloud computing is on the rise. And factors such as technology duplication, latency requirements, or data residency regulations justify this trend.
Anywhere Operations
This trend refers to a model that allows offering business solutions to customers from anywhere, and empowering employees to carry out their job functions regardless of where they are.
“A location-independent digital-first mindset is a prerequisite for anywhere operations.”

But it’s not just about operating remotely. The model must offer a unique, fluid and scalable experience. And, therefore, it implies changes at the level of technological infrastructure, management, security and government policies, and models of customer and employee participation.
This technological base is comprised of five blocks:
- Collaboration and Productivity – Workflow collaboration, meeting solutions, cloud office suites, digital whiteboard, and smart workspaces
- Secure remote access: multi-factor and passwordless authentication, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and identity as the new security perimeter
- Cloud and edge infrastructure: Distributed cloud, IoT, API gateways, AI at the edge, and edge processing
- Quantification of digital experience: digital experience monitoring, workplace analytics, remote support and contactless interactions
- Automation to support remote operations: artificial intelligence for IT operations (AIOps), endpoint management, SaaS management platforms, self-service and zero-touch provisioning.
Demand for digital services increased exponentially during the pandemic, and organizations that adopt digital business models to support their customers and employees will recover faster than others.
Cybersecurity mesh
This concept is closely linked to ” Anywhere operations” and is essential for the business to function safely. To operate from anywhere it is necessary to control access to data, devices, etc., from any location, people, etc. Now data is more distributed than ever and secure access must be ensured no matter where it is located.
Today, much of the company’s critical assets and documentation are outside the organization’s logical and physical perimeter. But, with the arrival of the pandemic, many of these goods have been moved to the homes of employees, partners and collaborators.
In this situation, companies must establish a security mesh that guarantees safe access to assets, regardless of their physical location, and that takes into account the permissions and restrictions established by role or user profile.
As a result of this new scenario, a transition to a model based on APIs is being observed, which is committed to security strategies based on the cloud such as ZTNA, CASB (Security Agents for Cloud Access) and SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) .
“As operations continue to evolve, the cybersecurity mesh will become the most practical approach to ensuring secure access and use of cloud-based applications and distributed data from uncontrolled devices.”
RESILIENT DELIVERY
This trend is about the ability of companies to adapt, or pivot, with agility in a dynamic business or IT environment.
The COVID 19 pandemic has created a highly volatile environment, and having the right skills, technical capabilities, processes and systems to constantly adapt to changing patterns is critical.
Consequently, organizations must be composable, use artificial intelligence, and continue with their digital transformation process, striving for hyper-automation.
Intelligent composable business
The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in business models that have been focused on efficiency for years. Organizations that were once efficient suddenly became fragile at a time when they needed to be flexible.
Faced with this situation, companies are obliged to face a change that allows them to move towards a more autonomous and efficient decision-making model. And to achieve this goal, technology platforms must move towards an architecture that facilitates access and content creation, prioritizing democratization and composable elements.
It is about composing complete solutions, based on different technological elements, that are inter-connected, and that would provide applications to solve the business issues, and offer a greater control and understanding of the data.
From an IT architecture point of view, a composable business solution is based on the use of APIs (Application Programming Interface).
“Composable business is a natural acceleration of the digital business that you live every day. It allows us to deliver the resilience and agility that these interesting times demand.”
Daryl Plummer
Artificial intelligence engineering
Gartner research reveals that almost 50% of artificial intelligence projects do not make it from prototype to production because organizations do not apply artificial intelligence engineering that the consultancy firm defines as “a discipline focused on the governance and life cycle management of a wide range of operationalized AI and decision models”. That includes machine learning, knowledge graphs, rules, optimization and linguistic and agent-based models.
AI engineering is built on three basic pillars: DataOps, MLOps, and DevOps.
- DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops) with the goal of shortening the system development lifecycle and providing continuous delivery with high-quality software.
- DataOps is an automated, process-oriented methodology used by data and analytics teams to improve quality and reduce data analysis cycle time.
- MLOps is a practice of collaboration and communication between data scientists and operations professionals to help manage the lifecycle of production machine learning (or deep learning).
What is responsible AI?
Responsible AI implies applying the principles of trust, transparency, ethics, fairness, interpretability, security, etc., to operations carried out with this technology.
Hyperautomation
Gartner defines hyperautomation as an effective combination of complementary sets of tools that can integrate functional and process silos to automate and augment business processes.
These technologies include the application of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), RPA, BPM, and data mining.
Organizations have clearly opted for hyperautomation in recent years, however, they still have many processes supported by obsolete and ineffective technologies.
In 2019, the CEOs who demanded greater advances in digital operations, considered legacy technologies as their main obstacle to achieve efficiency and democratization of process automation, and the required data integration. But in 2020, with the COVID 19 pandemic and many people working from home, digital excellence has become imperative and is evolving towards operational resilience.
“Hyperautomation is irreversible and inevitable. Everything that can and should be automated will be automated.”
Brian Burke, Research Vice President, Gartner
Competitive pressures for business efficiency, effectiveness, and agility are forcing organizations to address all possible scenarios for operations – back office, middle office, and front office. And organizations that resist change will have a hard time staying competitive.
The post Technology and business trends for 2021 appeared first on AuraQuantic.
