Process control’s ability to save costs and eliminate errors
Blog: Flokzu
In today’s business world, efficiency is paramount, and nothing assures it better than a reliable process control system. With the proper process control solution, it’s easier than ever to streamline operations, curtail expenses, and prevent mistakes. Discover how processing control can revolutionize your business.
What is Process Control?
Process control, in the context of Business Process Management (BPM), refers to the systematic approach of monitoring, managing, and optimizing business processes to ensure they are operating effectively and efficiently. This is essential for businesses to achieve their objectives, maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, and continuously improve their performance.
In other words, process control is about overseeing business processes to ensure they are functioning optimally, detecting issues, implementing corrective actions, and continuously improving processes to drive better performance and meet organizational goals. As a business analyst, understanding and applying process control principles can help you contribute to the success of your organization.
Types of Process Controls
Process management mechanisms can be classified into categories depending on their objectives and roles in an organization’s procedures. A Business Process Management (BPM) System aids in the execution and supervision of these regulatory measures. The main types of process controls and how a BPM Suite like Flokzu can assist are:
- Preventive Controls: These controls aim to minimize the risk of errors and deviations by preventing issues from occurring. A BPM Suite can help by automating and standardizing processes, ensuring that tasks are executed according to predefined rules and procedures. Additionally, it can oversee access permissions and implement the separation of responsibilities to thwart unauthorized activities.
- Detective Controls: These controls identify issues or deviations after they have occurred. A BPM Suite can assist by providing real-time monitoring and analytics based on key performance indicators (KPI’s), which helps detect problems early. It can also generate exception reports and trigger notifications when deviations are detected, allowing for prompt corrective action.
- Corrective Controls: Corrective controls rectify issues once they have been detected. A BPM Suite aids in uncovering the underlying causes of issues by offering access to past information and delivering valuable insights into processes. It can also help manage and track corrective action plans, ensuring timely resolution and preventing recurrence.
- Directive Controls: Directive controls guide behavior and ensure compliance with policies and regulations. A BPM Suite can store and manage policies, procedures, and guidelines, making them easily accessible to employees. It can also enforce compliance by automating checks and validations within processes, ensuring tasks are performed according to established rules.
- Physical Controls: Physical controls protect assets, information, and resources. A BPM Suite can help manage access to information by integrating with the process control system and implementing role-based access controls. It can also store and manage digital assets, ensuring their protection against unauthorized access or tampering.
- Administrative Controls: Administrative controls involve organizational measures to manage and monitor processes. A BPM Suite can assist by providing a centralized platform for managing processes, roles, and responsibilities, making it easier to monitor performance and maintain accountability. It can also generate performance reports and enable management oversight through dashboards and other visualizations.
Definitely, a BPM Suite can play a crucial role in implementing and managing the different types of process controls that you may need. By automating, standardizing, and monitoring processes, a BPM Suite can help organizations ensure the effective and efficient functioning of business processes while minimizing risks and maintaining compliance with regulations.
Who Uses Process Control and What for?
The main users of process controls are typically managers, supervisors, and process owners within an organization. These individuals play a crucial role in supervising and guaranteeing various business procedures’ smooth and productive operation. Their goal is to achieve operational excellence, maintain compliance with regulations, and continuously improve performance. Process controls are used by these users for various purposes, including:
- Ensuring Consistency: Process controls help maintain consistent performance across the organization by standardizing processes, reducing variability, and minimizing errors.
- Risk Management: Implementing process controls helps identify, mitigate, and manage risks associated with business processes, ensuring the organization’s goals are achieved without exposing it to unnecessary risks.
- Compliance: Process controls help organizations adhere to internal policies, industry standards, and regulatory requirements, which is crucial for maintaining a strong reputation, avoiding fines, and ensuring legal compliance.
- Performance Monitoring: Controls enable managers and process owners to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and other relevant metrics, providing insights into process performance and highlighting areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Process controls facilitate the identification of inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and other issues within business processes. This data enables ongoing strategy enhancement and fine-tuning procedures in the long run.
- Accountability: Implementing process controls helps establish clear roles and responsibilities, ensuring that employees understand their tasks and are held accountable for their performance.
Industries that Utilize Process Control
Process controls are used across various industries, as they play a crucial role in ensuring the effective and efficient functioning of business processes, managing risks, and maintaining compliance.
Manufacturing companies
Historically, manufacturing companies relied more heavily on process controls due to the nature of their operations, regulatory requirements, or the level of complexity involved in their processes. For example:
- Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences industries are highly regulated and require strict adherence to quality standards and good manufacturing practices. Process controls are essential in ensuring product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
- The oil and gas industry handles intricate procedures, perilous substances, and considerable ecological threats. Process controls are vital in managing these risks, optimizing production, and ensuring the safe operation of facilities.
- Chemical manufacturing involves handling hazardous materials and requires strict process controls to ensure safety, product quality, and environmental compliance.
- Food and Beverage is governed by rigorous health and safety rules and high quality requirements. The sector maintains product excellence, uniformity, and adherence to food safety guidelines through effective process management.
- Aerospace and Defense: These industries involve highly complex processes and require strict quality and safety standards. Process controls help ensure product reliability, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Service companies
Process controls are equally important in service companies as they are in manufacturing organizations. Service companies also need to ensure the effective and efficient functioning of their business processes, manage risks, and maintain compliance with regulations. Some examples of process controls in service companies include:
- Banking and Financial Services: In this industry, process controls are crucial for managing risks such as credit risk, operational risk, and fraud risk. They guarantee precise fiscal documentation, preserve information safety, and comply with legal mandates, including anti-money laundering (AML) and customer identification protocols (KYC) rules.
- Healthcare Services: In healthcare facilities, procedural management safeguards the well-being of patients, secures confidential health data, and upholds adherence to numerous regulatory requirements and norms, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Information Technology Services: Within the realm of IT solutions, procedural regulations serve as a means to oversee project execution, ascertain superior software development quality, sustain data protection, and adhere to relevant industry benchmarks, including ISO/IEC 27001 pertaining to information security administration.
- Professional Services: In industries like consulting, legal, and accounting services, process controls help manage client engagements, ensure the quality of deliverables, maintain data privacy, and adhere to professional and ethical standards.
- Human Resources Services: In HR services, process controls help manage recruitment, onboarding, performance management, payroll processing, and compliance with labor laws and regulations.
- Education Services: Process controls in educational institutions ensure the quality of educational programs, maintain accreditation standards, and comply with regulatory requirements.
The Importance of Process Control
Understanding the importance of process control is vital in the modern industry. It’s a dynamic strategy that can drastically slash costs and eradicate errors. In order to fully enjoy these advantages, however, it is essential for you to delve into the heart of process control engineering.
Embracing process control is the first step towards more streamlined, error-free operations. It’s not just about saving costs; it’s about enhancing the overall quality of your processes and making your business more competitive, resilient, and adaptable in the ever-evolving market landscape. Remember, in the process control world, the importance can never be understated. It’s the secret ingredient for business success.
Benefits of Process Control
Implementing good process controls can provide numerous benefits to an organization:
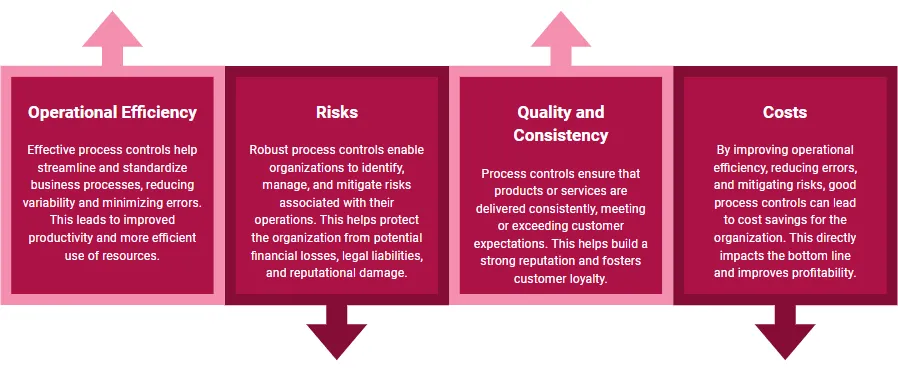
We can also find benefits in regulatory compliance, given that good process controls help organizations adhere to industry standards, regulatory requirements, and internal policies. This is crucial for maintaining a strong reputation, avoiding fines, and ensuring legal compliance.
Additionally, process controls provide insights into the performance of business processes, enabling data-driven decision-making. This allows C-level executives to make informed strategic decisions that drive organizational growth and success.
Finally, having good process controls increases accountability, helps establish clear roles and responsibilities, ensuring that employees understand their tasks and are held accountable for their performance.
Risks of Inadequate Process Control
In the world of industry and technology, understanding and implementing the control process is a must. However, it’s about more than just knowing how to define process control but also about comprehending the risks of not having an adequate control process.
Inadequate process control can lead to various issues, including operational inefficiencies, unexpected downtime, increased costs, and a heightened risk of errors. A subpar control process might let small issues slip through unnoticed, eventually snowballing into more significant problems.
Let’s illustrate this with an example. Consider a production line where the control process needs to be thoroughly monitored or adjusted. Small variances might creep in unnoticed, gradually affecting the output quality. Before long, this could result in product recalls, tarnished brand image, and lost customers – all adding to the overall costs.
The importance of process control is truly indispensable. It’s a safeguard against potential mishaps, a cost-saving driver, and a booster for operational efficiency. Embracing an efficient control process is the secret to keeping your operations running smoothly while reducing costs and eliminating errors. It’s not just about the ‘how,’ but also about understanding the ‘why.’ Hence, if you wish to avoid the risks above, the path to superior process control is worth embarking on.
Process Control Examples
Consider a procurement process in which an organization needs to automate approvals for purchase requests. In this scenario, various types of process controls can be implemented using Flokzu BPM Suite, ensuring compliance with internal policies and minimizing the risk of unauthorized purchases.
- Preventive Controls: Flokzu can help establish and enforce approval limits based on the request value or the employee’s role within the organization. By defining these limits, the Process Engine ensures that only authorized personnel can approve purchase requests within their designated authority. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized approvals and potential financial losses.
- Detective Controls: The BPM Suite can monitor the approval process in real-time, generating reports and notifications when deviations or exceptions occur, such as a delayed approval or approval that exceeds the designated limits. This enables supervisors to promptly recognize and resolve any concerns, guaranteeing that the procedure stays compliant and effective.
- Corrective Controls: If any deviations or issues are detected, Flokzu can help initiate corrective actions, such as re-routing the request to the appropriate approver or implementing additional review steps. This ensures that any issues are promptly resolved and prevents their recurrence.
- Directive Controls: The BPM Suite can store and manage guidelines, policies, and procedures related to the approval process, making them easily accessible to employees. This ensures that employees are aware of the rules and expectations, promoting compliance and minimizing the risk of errors or deviations.
A low-code / no-code BPM Suite is particularly relevant in this context because it allows non-technical users, such as business analysts and process owners, to design, implement, and manage the approval process without the need for programming expertise. This empowers them to take ownership of the process, make changes as needed, and ensure that the controls are effectively implemented and monitored.
Process Control with Flokzu
Flokzu BPM Suite is designed to help organizations implement and manage various types of process control within their business processes. Some of the key process controls provided by Flokzu BPM Suite include:
- Workflow Automation: Flokzu allows you to define and automate workflows for different processes, ensuring tasks are executed in a standardized and consistent manner. This functions as a protective measure, reducing the likelihood of inaccuracies and discrepancies.
- Role-based Access Control: Flokzu enables you to manage access rights and permissions based on user roles. This helps establish the segregation of duties, ensuring that only authorized personnel can perform specific tasks.
- Real-time Monitoring and Analytics: Flokzu provides real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities, allowing you to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify bottlenecks or deviations in your processes. This serves as an investigative safeguard, allowing you to implement remedial measures as needed.
- Notifications and Alerts: Flokzu can generate notifications and alerts when specific events or conditions are met, such as deviations from predefined rules or pending tasks that exceed a certain duration. This helps you stay informed about any issues that require attention.
- Document Management: Flokzu allows you to store, manage, and share documents related to your processes, ensuring that relevant information is accessible and securely stored.
- Process Versioning and Audit Trails: Flokzu supports process versioning and maintains audit trails, providing you with historical data and insights into changes made to your processes. This can help with root cause analysis and continuous improvement efforts.
- Compliance Enforcement: Flokzu can help enforce compliance with internal policies, industry standards, and regulatory requirements by automating checks and validations within your processes.
Please note that while Flokzu provides various process control features, it is essential to understand your organization’s specific requirements and tailor the implementation of these controls accordingly. In certain instances, supplementary instruments or interconnected systems might be essential for attaining the optimal degree of procedural regulation.
No-code Capabilities to Implement Good Controls
The no-code capabilities in Flokzu are indeed relevant to implementing good process controls. They enable non-technical users, such as business analysts, managers, or process owners, to design, implement, and manage business processes and process controls without needing programming expertise. This can lead to quicker implementation of process controls and more effective collaboration between business and IT teams.
No-code enables organizations to implement process controls more quickly by eliminating the need for custom coding. This can help organizations achieve compliance, reduce risks, and improve operational efficiency in a shorter time frame.
Complimentary, flexibility, and adaptability are crucial too. No-code capabilities in Flokzu make it easy for users to modify and adapt processes and process controls as business requirements change or new regulations are introduced. This ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to evolving needs.
Finally, implementing process controls using a no-code platform can reduce the costs associated with custom development and maintenance, as non-technical users can manage and update processes without the need for specialized IT resources.
The Importance of Implementing Your Own Controls
Defining your own process controls is a crucial aspect of differentiating your organization from competitors. By tailoring process controls in Flokzu to the unique needs and goals of your business, you can enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall performance of your operations, which sets you apart in the market.
A primary advantage of tailoring your process management protocols is tackling the distinct risks and hurdles your establishment encounters. By identifying and mitigating these risks, you can minimize potential disruptions and losses, ensuring that your business remains resilient in a competitive environment.
Moreover, when you design process controls that align with your organization’s objectives and strategies, you can streamline your operations, reduce waste, and optimize resource utilization. This can lead to improved productivity and cost savings, which directly impact your bottom line and enhance your competitive advantage.
Custom process controls also help you maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards that may be unique to your organization. By adhering to these requirements, you can avoid costly fines and penalties, protect your reputation, and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
One more benefit of establishing custom process controls is that it cultivates an environment of ongoing enhancement throughout your institution. When you regularly evaluate and refine your processes and controls – what you can do quickly using Flokzu’s no-code capabilities – you can identify new opportunities for innovation and growth, ensuring that your business stays ahead of the curve and adapts to changing market conditions.
Integrating Flokzu with Other Tools
You can integrate Flokzu with other specific control tools to enhance process controls and overall effectiveness. Integrating Flokzu with external tools can help you expand its capabilities, automate data exchange, and streamline various aspects of your processes.
Flokzu provides integration options through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and webhooks, which can be used to connect it with other control tools, software applications, or process control service.
Conclusion
Process of control plays a vital role in the administration of business procedures, guaranteeing the seamless and productive performance of a company’s activities. Implementing various types of process controls, such as preventive, detective, and corrective controls, helps manage risks, maintain compliance, and drive continuous improvement.
Using a BPM Suite like Flokzu can streamline the implementation of process controls, enabling non-technical users to design, manage, and monitor processes with ease. Its no-code capabilities empower organizations to take ownership of their processes and controls, leading to faster implementation, lower costs, and better adaptability. Integrating Flokzu with other control tools and systems further enhances the effectiveness of your process controls, providing a more comprehensive and tailored approach to managing your business processes.
Customizing process controls to suit your organization’s unique needs and goals is essential for differentiating from competitors, ensuring resilience, and fostering long-term growth and success.
FAQs
What are examples of process control?
Process control is pivotal across various industries, ensuring consistency, quality, and efficiency in operations. For instance, automated process control systems monitor and adjust machinery settings in manufacturing to ensure product uniformity. In the chemical industry, process control optimizes chemical reactions for desired outputs. Even in our daily lives, we employ process control unconsciously. For instance, deciding how much food to consume based on past experiences is a form of predictive process control. Thus, the control and process mechanisms are integral to industrial and everyday contexts.
What is meant by process control?
Process control refers to the ability to observe, manipulate, and guide a process to obtain a desired outcome, primarily in various industries, to optimize performance and uphold product quality. This controlling process definition implies that it is a system of monitoring and intervening to ensure the process stays within predetermined parameters. Utilizing process control enhances efficiency, minimizes human error, allows for detailed analysis, and assists in constant changes to production.
What are the types of in process controls?
In-process controls are essential to ensure smooth operations and maintain quality standards. Several types of in-process controls exist, including preventive, detective, corrective, physical, and administrative controls. Preventive controls aim to avoid potential issues or disruptions, while detective controls identify and expose existing problems. Corrective controls are implemented to rectify the identified issues and restore process efficiency. Physical controls involve concrete barriers that limit access and protect assets, whereas administrative rules include policies, guidelines, and procedures followed within an organization to maintain systematic functionality.
What are the 4 basics of process control?
The four basics of process control revolve around managing and optimizing industrial processes to ensure efficiency, quality, and safety. They include:
- Measurement: Collecting accurate and continuous data on process variables like temperature, pressure, and flow rate to monitor operations in real-time.
- Control algorithm: Implementing rules or logic to analyze collected data and decide on the necessary adjustments to maintain desired process conditions.
- Actuation: Executing changes in the process through control devices, such as valves or pumps, depending on the control algorithm’s output.
- Feedback loop: Continuously monitoring and adjusting the process based on the performance of previous adjustments, maintaining stable and optimum process conditions.
These four basics of process control form the foundation for automation control solutions, which involve utilizing advanced technology to orchestrate, manage, and optimize industrial processes.
The post Process control’s ability to save costs and eliminate errors appeared first on Flokzu.