Cloud computing and the differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
Blog: AuraQuantic Blog
Cloud computing, or simply “cloud” refers to a very widespread technological trend among users and companies, consisting of a set of services over the Internet.
What is Cloud Computing?
Technically speaking, cloud computing is a computational paradigm designed to offer services through a network, typically the Internet. Cloud computing has made it possible for users to consume resources and services on demand, through a high-speed connection.
A common myth is one that defines the cloud as “someone else’s computer.” This is not true, since when we talk about cloud we are talking about a set of high-capacity computers connected through a high-speed network, which can work together to easily scale if required.
Cloud Computing features
To be classed as cloud computing, at the very least, the services must offer the features listed below.
On-demand service
The user must be able to access and consume the service through the internet when required.
Access and availability
To comply with the previous point, it is important that the service is always available and accessible from anywhere, via internet connection.
Flexibility and scalability
The cloud service must be adaptable to the business’ computational demands; that is, if the number of users of a certain application increases considerably, the system must be able to allocate more resources automatically, to respond to this rise.
Virtualization
It consists of creating virtual machines; that is, a layer that allows multiple operating systems (OS) to be installed on the same machine, so that the hardware capabilities can be shared.
Virtualization optimizes the use of the systems and is a fundamental part of cloud computing since the entire hardware is not reserved for single consumer’s processes (which is usually inefficient most of the time), instead it is used by different customers.
Security
From backup mechanisms to firewalls and antimalware mechanisms, the cloud must provide solutions that guarantee security and continuity of service, even in very adverse scenarios.
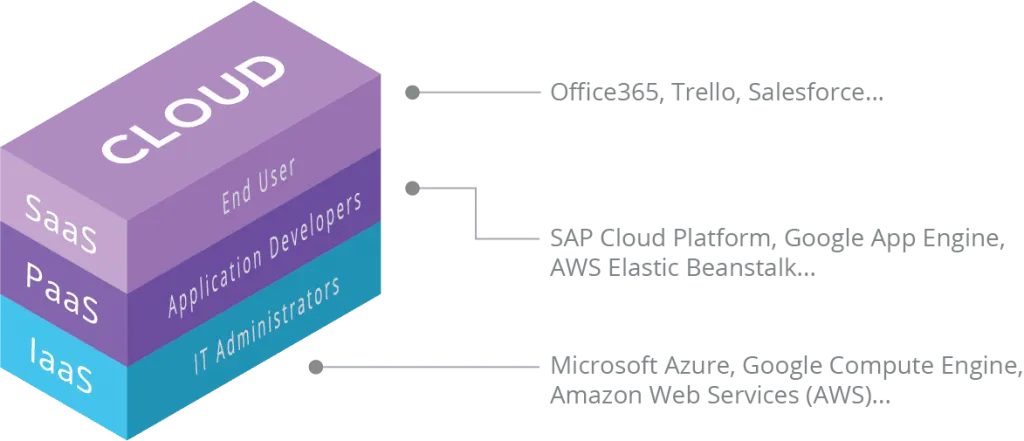
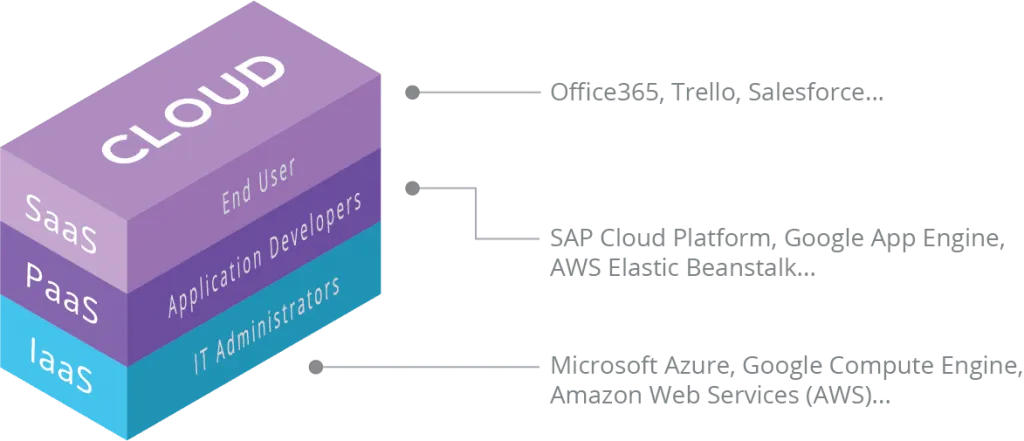
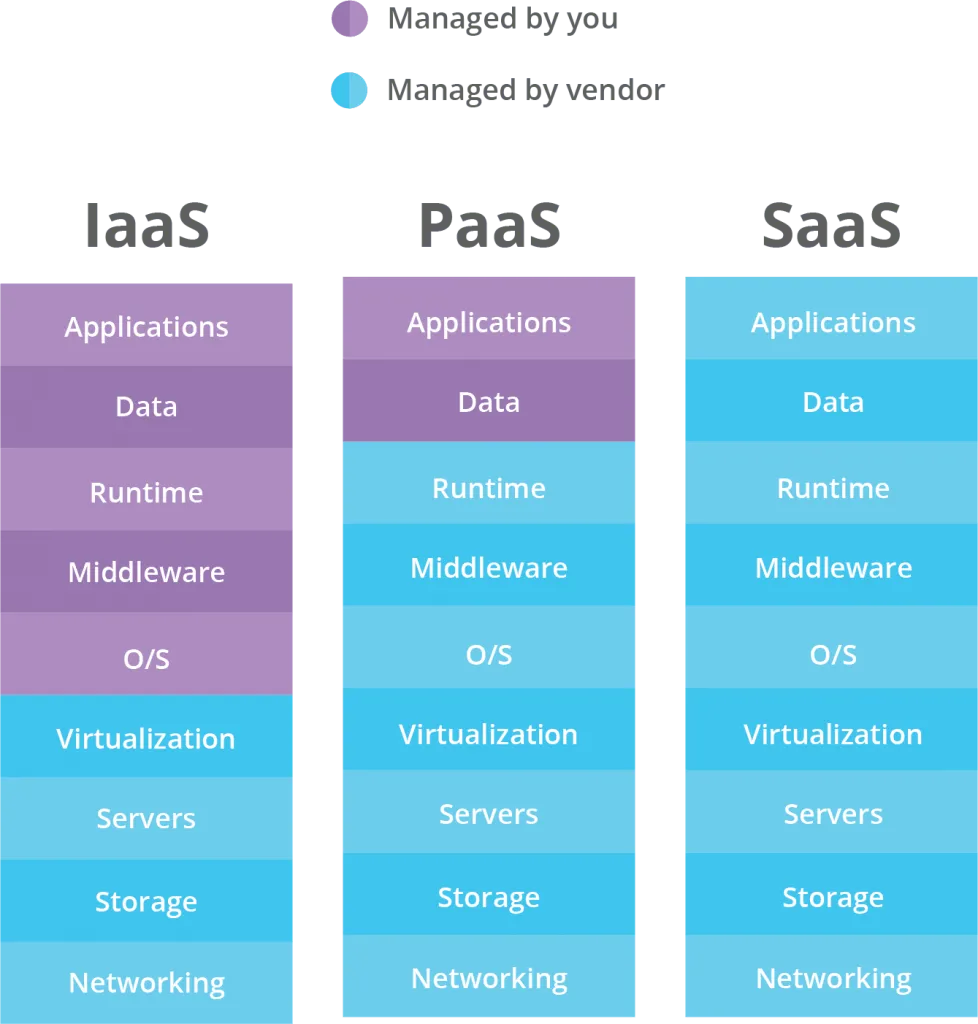
Differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
A typical categorization within Cloud services is the one that divides its different modalities. Currently, there is a tendency to differentiate 3 different cloud service modalities: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
This is the architect-oriented level of software solutions and it encompasses everything related to the necessary infrastructure, including hardware and software. This layer includes the cloud services and solutions offered by large companies in the technology sector such as Microsoft, Amazon or Google, through their Azure products, AWS (Amazon Web Services) and GCP (Google Cloud Platform), respectively.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a Service is aimed at programmers and technical users; It consists of platforms that facilitate the development of applications that end users can consume directly in the cloud. An example of PaaS is Firebase.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
This is software for the end user, which can be used from the cloud, without the need to install anything. A user with an internet connection, and generally using a browser, accesses the service and consumes it; This can be a video streaming platform, a social network, an online video game, a business management platform, etc.
Cloud Types
Apart from the 3 types of Cloud services mentioned above, another differentiation often made is that of cloud types.
Private
A company installs all its infrastructure, connects computers, defines how services will work and installs the software it deems necessary.
Public
This is a cloud that everyone can access, for example, the cloud service offered by large providers such as Microsoft, AWS or Google. Sometimes a layer of services is even offered for free and charges start from a certain level of usage.
Hybrid
The hybrid cloud has a private part and a public part; In other words, a company could decide to have certain data stored and available on a private cloud and other services on a public cloud.
Cloud Use Cases
Today the use of cloud services is very widespread, and seen in practically any field and level: public services, companies, end users, etc.
In the case of web services, companies tend to buy cloud solutions instead of classic hosting solutions. Classic hosting solutions have very limited freedom in the use of resources and they do not offer the same scalability, security or continuity capabilities.
Business management
One of the most common uses of the cloud is by companies using SaaS-type business management applications, be it email through the Office 365, CRM or ERP solutions such as Salesforce or SAP.
Videogames and entertainment
One of the most demanding branches (computationally speaking) is that related to video games and entertainment, entering into this category are cooperative online games (which easily reach tens of thousands of active users at the same time) and Netflix-type streaming platforms.
The cases mentioned are interesting examples of the cloud’s capabilities, since the majority of users concentrate at certain times of the day and differently depending on the country, which demonstrates the scalability and flexibility of the cloud platform.
Storage
Although it is something we have been using for many years, data storage is still the most widely used cloud service. From Dropbox to Amazon S3, Google Drive or Microsoft’s OneDrive, these solutions are very popular for both individual users and companies.
Computing power
As mentioned earlier, the cloud is not a single machine; it is many interconnected machines capable of providing a service with high availability. However, there are also times when the computing capacity of these machines comes together to carry out very complex algorithms and calculations for example, 3D video rendering (via render farms), engineering simulations, or Machine Learning algorithms.
Artificial Intelligence and ML
Difficult to implement and with algorithms too complex for a single machine to run, the main cloud providers have seen business in the implementation of Artificial Intelligence leveraging their own infrastructures. Thus, large companies such as Amazon, Microsoft or Google offer Artificial Intelligence services to users who consume their IaaS, adding value to their cloud offering.
Find out why AuraPortal Cloud is the preferred solution to create applications, automate processes and manage business ecosystems in the Cloud:
The post Cloud computing and the differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS appeared first on AuraPortal.