A practical guide to process automation
Blog: AuraQuantic Blog
Business process automation, also known as intelligent process automation or digital process automation, is the technology-enabled automation of complex business processes. Here is a practicle guide to help your process automation project.
Many enterprises are feeling the pressure to meet new market challenges, improve the customer experience and ensure compliance with ever-changing regulations. However, many projects are failing to deliver the desired outcomes and enterprises are missing out on strategic business value because they have integrated software as a stand-alone solution or end up with different siloed solutions working in isolation. Let’s take RPA and AI for example; they are extremely powerful technologies but have drawbacks that all boil down to the same point: by themselves, they can only impact individual work tasks. This is where Process automation using low-code platforms comes in. Intelligent process automation or hyperautomation, as it is sometimes called, can be used to combat these challenges and leverage the benefits of a wide range of technology.
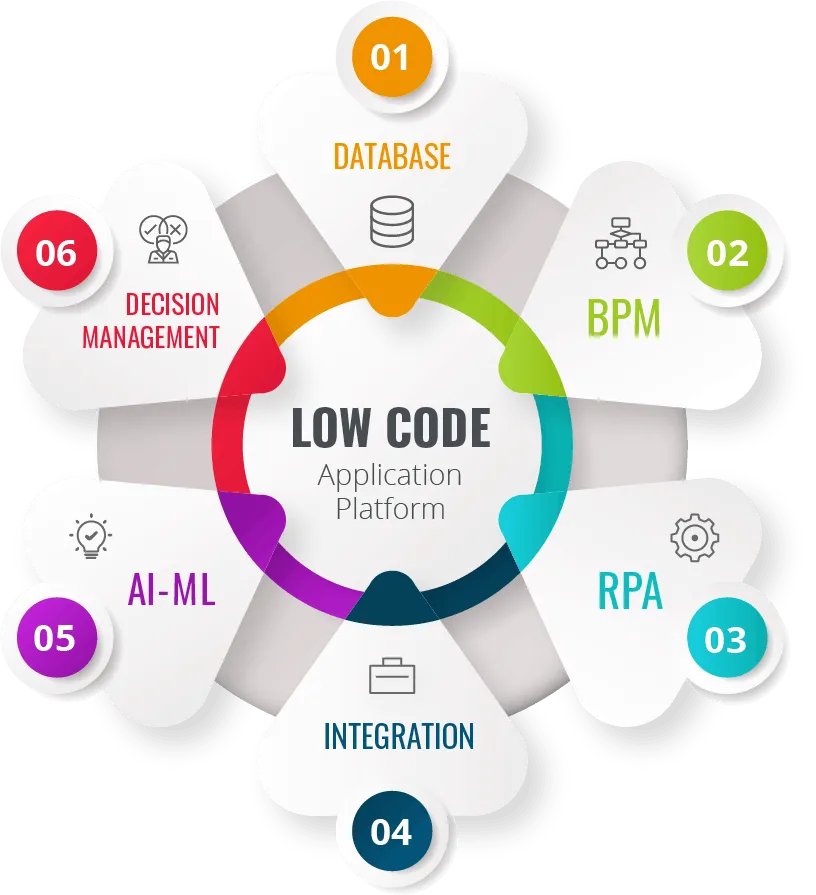
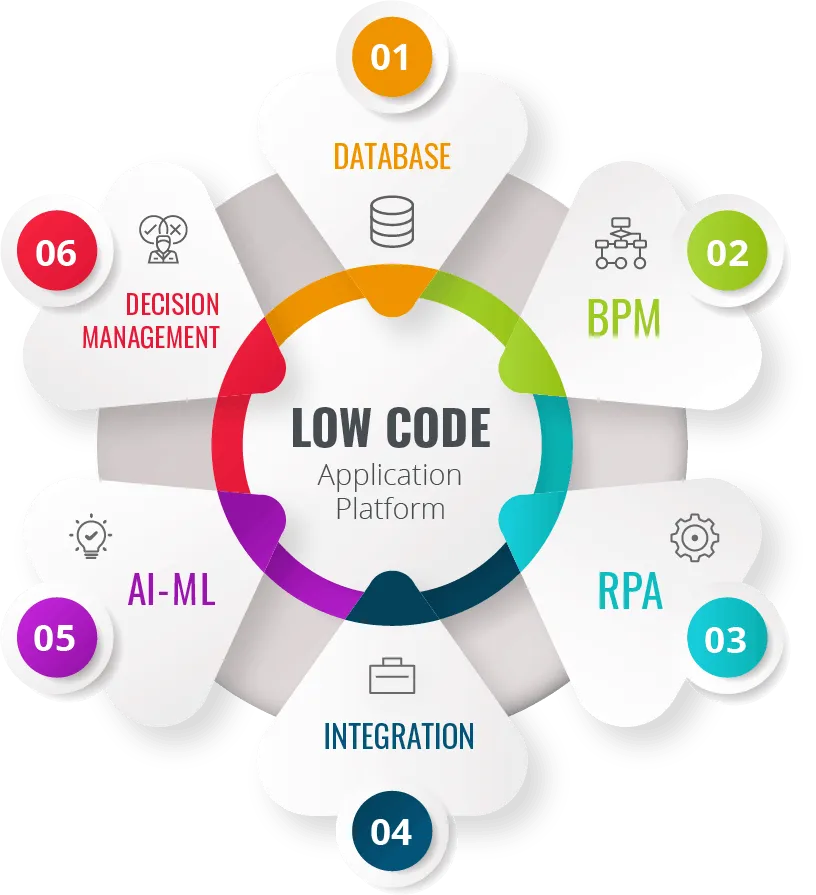
Main elements of process automation
Process Automation can involve a group of software technologies that work seamlessly together to manage, automate and integrate business processes in an enterprise. The main trend is to have all technology integrated in one platform to provide a single source of truth for all company data. This technology ecosystem often includes AI, ML, RPA, workflow management, decision management, BPM and integration.
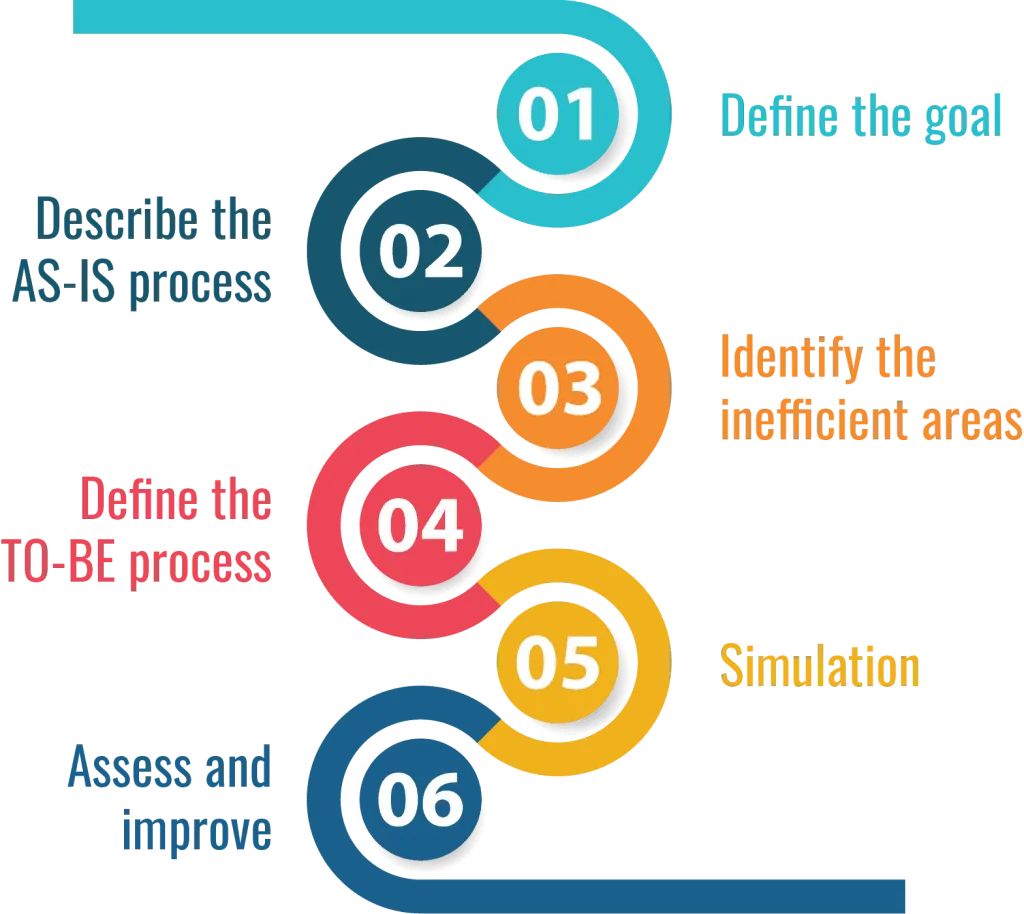
Typical steps for process automation.
1. The first step is to define the goal or the problem that you need to solve.
It is recommendable to start small and have clear goals. Results must be noticeable to get all workers on board and scale for future Project.
2. Describe the AS-IS process, documenting how the process is currently completed.
It is important to understand the current state of the process, who participates and what their work involves.
3. Identify the inefficient or ineffective areas.
Defining the AS-IS process may highlight inefficiencies such as repetitive tasks that could be performed faster using RPA, or a slow decision-making process that could be better managed with business rules and decision management, etc.
4. Design how the process should run, the TO-BE process.
Using a low-code platform this can be done without programming code, using drag and drop to draw the process. Some platforms make it easy for the business user by providing connectors and native integration to easily incorporate other technologies at this point, such as SAP, RPA and AI connectors.
5. Simulate the process if necessary, changing variables until you are happy with the outcome.
Simulation can be used to pinpoint bottlenecks, determine how many workers are required or calculate production times, etc. before putting the application in execution.
6. Insert control points and key performance indicators to assess and continually improve the process.
It is extremely important to include well-positioned control points. The data generated from these control points will provide key information about the process, which can be used for monitoring and process improvement.
Achieving process automation leveraging an integrated business ecosystem will minimize the number of user interfaces that employees need to learn to use and will provide a fast and low-cost path to automation. The typical steps may vary depending on the enterprise but failing to properly plan and assess the process will not produce the optimal result and can lead to the failure of the project. Indeed, there is much truth behind Benjamin Franklin’s adage, “failing to plan is planning to fail”.
Low-code application platforms are becoming increasingly powerful, addressing more enterprise use cases, making it easier for the users and providing rapid application delivery to the advantage of businesses everywhere.
The post A practical guide to process automation appeared first on AuraPortal.